BiRewire is an R package implementing high-performing routines for the randomisation of bipartite graphs preserving their node degrees (i.e. Network Rewiring), through the Switching Algorithm (SA) [1]. BiRewire analytically estimates the number of Switching Steps to be performed in order for the similarity between the original network and its rewired version to reach a plateau (i.e. to achieve the maximal level of randomness) according to the lower bound derived in Gobbi et al [see Publications below.]
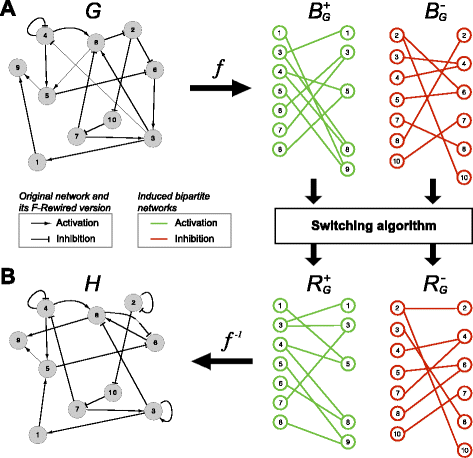
This package is particularly useful for the randomisation of ’0-1’ tables (or presence-absence matrices) in which the distributions of non-null entries (i.e. presence distributions) must be preserved both across rows and columns. By considering these tables as incidence matrices of bipartite graphs then this problem reduces to bipartite network rewiring.
For example, by modeling a genomic dataset as a binary event matrix (BEM), in which rows correspond to samples, columns correspond to genes and the (i,j) entry is non-null if the i-th sample harbours a mutation in the j-th gene, then with BiRewire is possible to randomise the dataset preserving its mutation rates both across samples and genes. This is crucial to preserve tumour specific alterations, dependencies between gene-mutations and etherogeneity in mutation/copy-number-alteration rates across patients. Large collections of such randomised tables can be then used to approximate samples from the uniform distribution of all the possible genomic datasets with the same mutation-rates of the initial one. Finally this data can be used as null model to test the statistical significance of several combinatorial properties of the original dataset: for example the tendency of a group of genes to be co- or mutually-mutated. Extension to the general case of undirected networks (not bipartite) is also provided.
Please use this reference to cite BiRewire:
Iorio, F., Bernardo-Faura, M., Gobbi, A., Cokelaer, T., Jurman, G. and Saez-Rodriguez, J. (2016). Efficient randomization of biological networks while preserving functional characterization of individual nodes. BMC Bioinformatics, 17(1), p.542..
@article{iorio2016efficient,
title={Efficient randomization of biological networks while preserving functional characterization of individual nodes},
author={Iorio, Francesco and Bernardo-Faura, Marti and Gobbi, Andrea and Cokelaer, Thomas and Jurman, Giuseppe and Saez-Rodriguez, Julio},
journal={BMC Bioinformatics},
volume={17},
number={1},
pages={542},
year={2016},
publisher={BioMed Central}
}
[1] Milo R, Kashtan N, Itzkovitz S, et al. On the uniform generation of random graphs with prescribed degree sequences. Arxiv preprint cond-mat/0312028 2003