Applies modular normalization including 80% filtering rule, total-ion count normalization, missing value imputation, and outlier detection using Hotelling's T2 test.
Usage
processing(
data,
metadata_sample = NULL,
metadata_info = c(Conditions = "Conditions"),
featurefilt = "Modified",
cutoff_featurefilt = 0.8,
tic = TRUE,
mvi = TRUE,
mvi_percentage = 50,
hotellins_confidence = 0.99,
core = FALSE,
save_plot = "svg",
save_table = "csv",
print_plot = TRUE,
path = NULL
)Arguments
- data
SummarizedExperiment or data frame. If SummarizedExperiment, metadata_sample is extracted from colData. If data frame, provide unique sample identifiers as row names and metabolite numerical values in columns with metabolite identifiers as column names. Use NA for undetected metabolites.
- metadata_sample
Data frame (optional). Only required if data is not a SummarizedExperiment. Contains information about samples, combined with input data based on unique sample identifiers used as row names. Must contain Conditions column. If experiment has no multiple conditions, assign all samples to same condition. Default: NULL.
- metadata_info
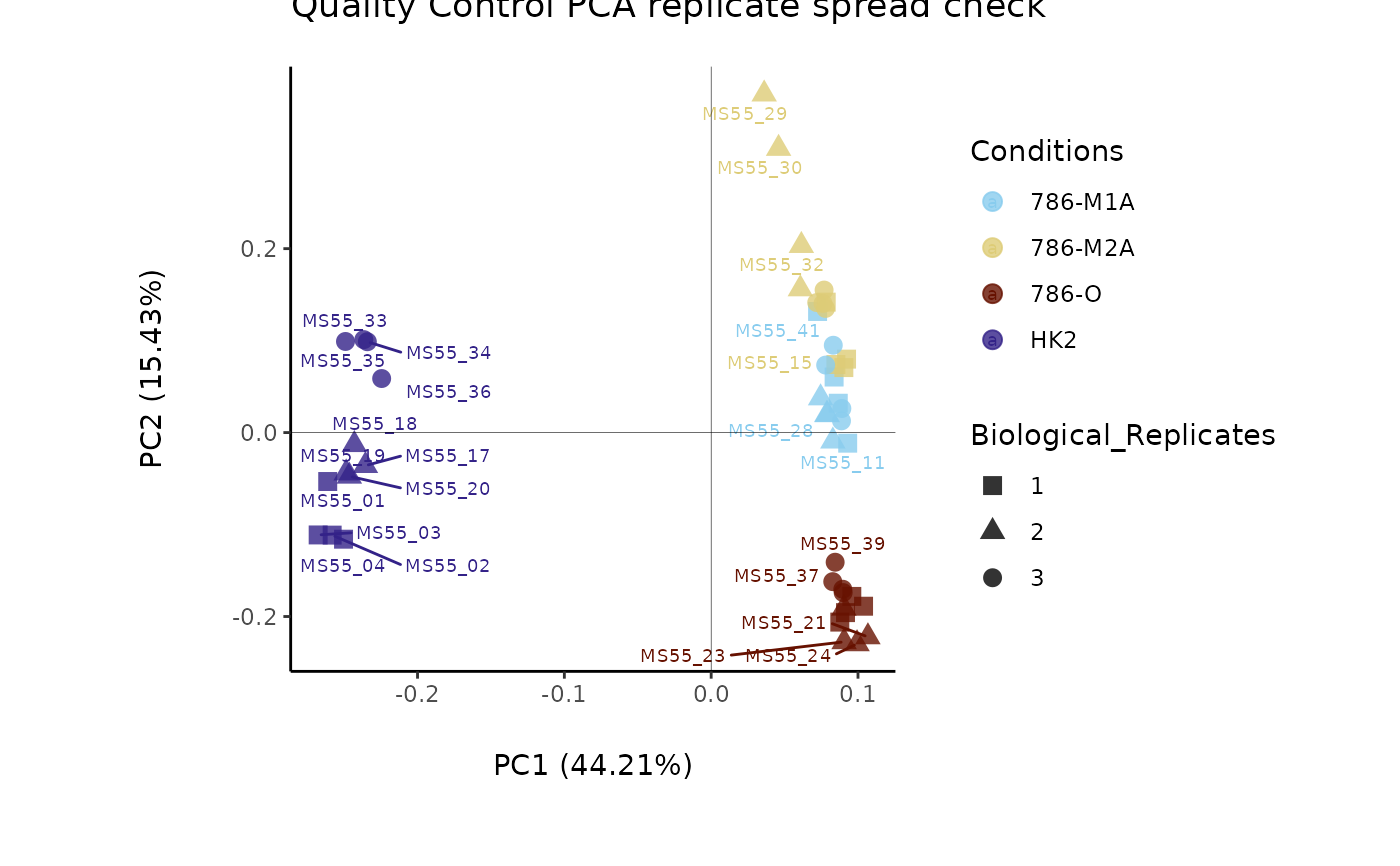
Named character vector (optional). Contains names of experimental parameters: c(Conditions="ColumnName", Biological_Replicates="ColumnName"). Column "Conditions" (mandatory) contains sample conditions (e.g., "N"/"T" or "Normal"/"Tumor"), used for feature filtering and PCA color coding. Column "BiologicalReplicates" (optional) contains numerical values. For core=TRUE, must also add core_norm_factor="ColumnName" and core_media="ColumnName". Column core_norm_factor is used for normalization; core_media specifies media controls in Conditions. Default: c(Conditions="Conditions").
- featurefilt
Character (optional). If NULL, no feature filtering is performed. If "Standard", applies 80% filtering rule (Bijlsma et al., 2006) on metabolite features across whole dataset. If "Modified", filtering is done per condition and Conditions column must be provided (Yang et al., 2015). Default: "Standard".
- cutoff_featurefilt
Numeric (optional). Percentage threshold for feature filtering. Default: 0.8.
- tic
Logical (optional). Whether total ion count normalization is performed. Default: TRUE.
- mvi
Logical (optional). Whether missing value imputation (MVI) based on half minimum is performed. Default: TRUE.
- mvi_percentage
Numeric (optional). Percentage (0-100) of imputed value based on minimum value. Default: 50.
- hotellins_confidence
Numeric (optional). Confidence level for outlier identification in Hotelling's T2 test. Default: 0.99.
- core
Logical (optional). Whether consumption-release experiment was performed and core value should be calculated. If TRUE, provide normalization factor column "core_norm_factor" in metadata_sample where Conditions column matches. The normalization factor must be numerical value from growth rate (growth curve) or growth factor (ratio of cell count/protein quantification at start vs. end point). Additionally, control media samples must be available in data and defined as "core_media" in Conditions column of metadata_sample. Default: FALSE.
- save_plot
Character (optional). File type of output plots: "svg", "png", "pdf". If NULL, plots are not saved. Default: "svg".
- save_table
Character (optional). File type of output table: "csv", "xlsx", "txt". If NULL, tables are not saved. Default: "csv".
- print_plot
Logical (optional). Whether to print overview of resulting plots. Default: TRUE.
- path
Character (optional). Path to folder where results should be saved. Default: NULL.
Examples
data(intracell_raw_se)
ResI <- processing(
data = intracell_raw_se,
metadata_info = c(
Conditions = "Conditions",
Biological_Replicates = "Biological_Replicates"
)
)
#> feature_filtering: Here we apply the modified 80%-filtering rule that takes the class information (Column `Conditions`) into account, which additionally reduces the effect of missing values (REF: Yang et. al., (2015), doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00004). Filtering value selected: 0.8
#> 3 metabolites where removed: AICAR, FAICAR, SAICAR
#> Missing Value Imputation: Missing value imputation is performed, as a complementary approach to address the missing value problem, where the missing values are imputing using the `half minimum value`. REF: Wei et. al., (2018), Reports, 8, 663, doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-19120-0
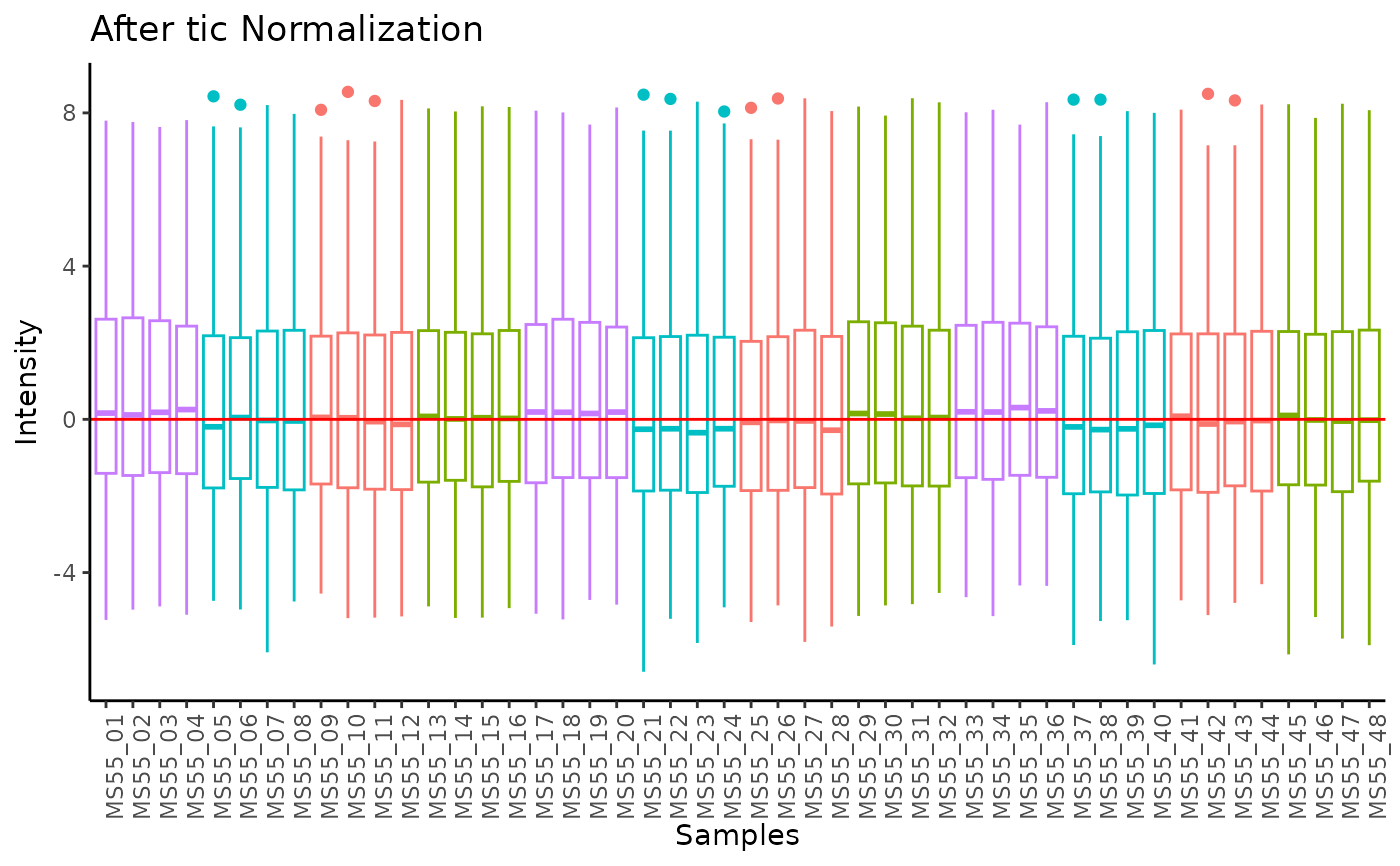
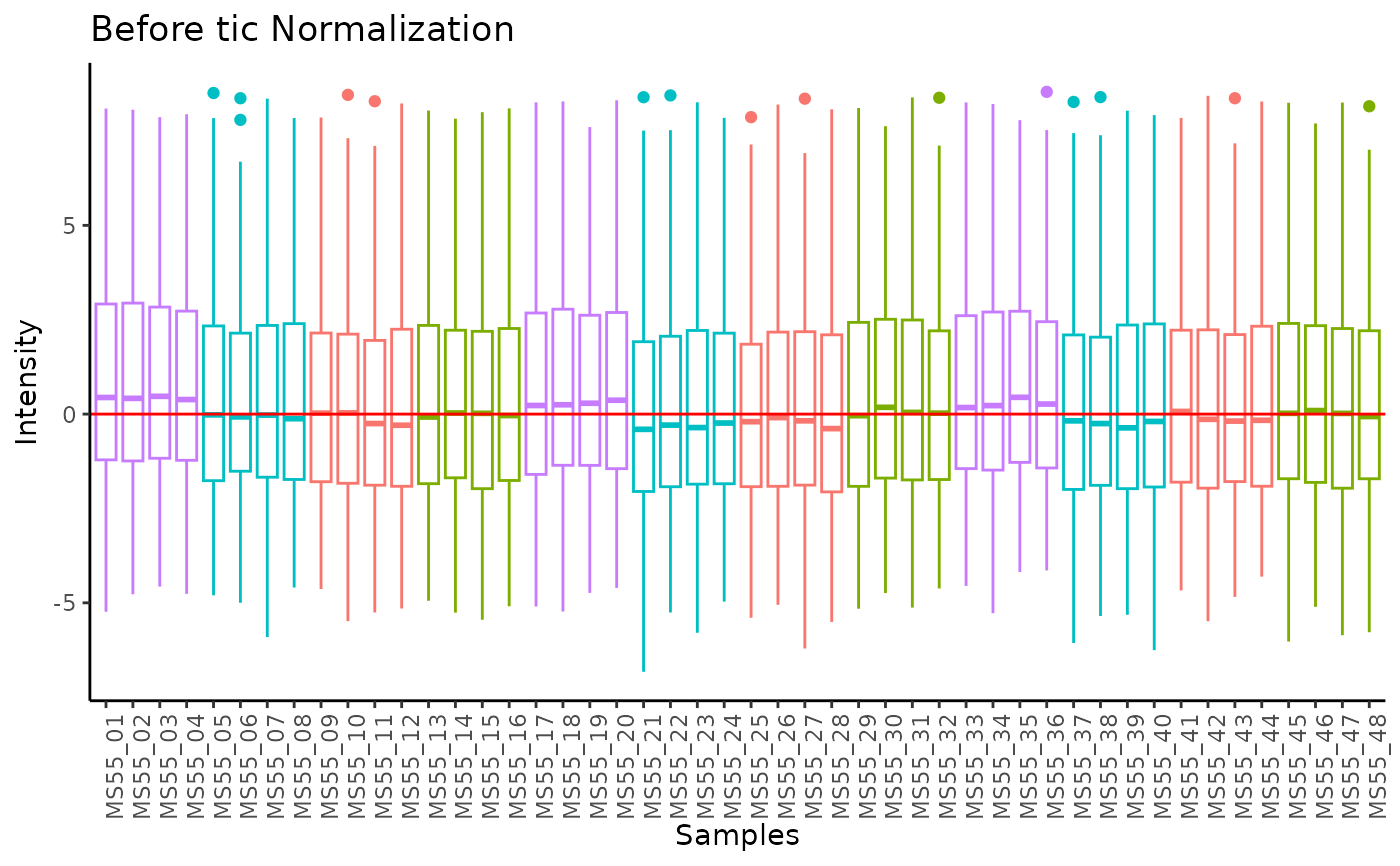
#> total Ion Count (tic) normalization: total Ion Count (tic) normalization is used to reduce the variation from non-biological sources, while maintaining the biological variation. REF: Wulff et. al., (2018), Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 9, 339-351, doi:https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2018.98022
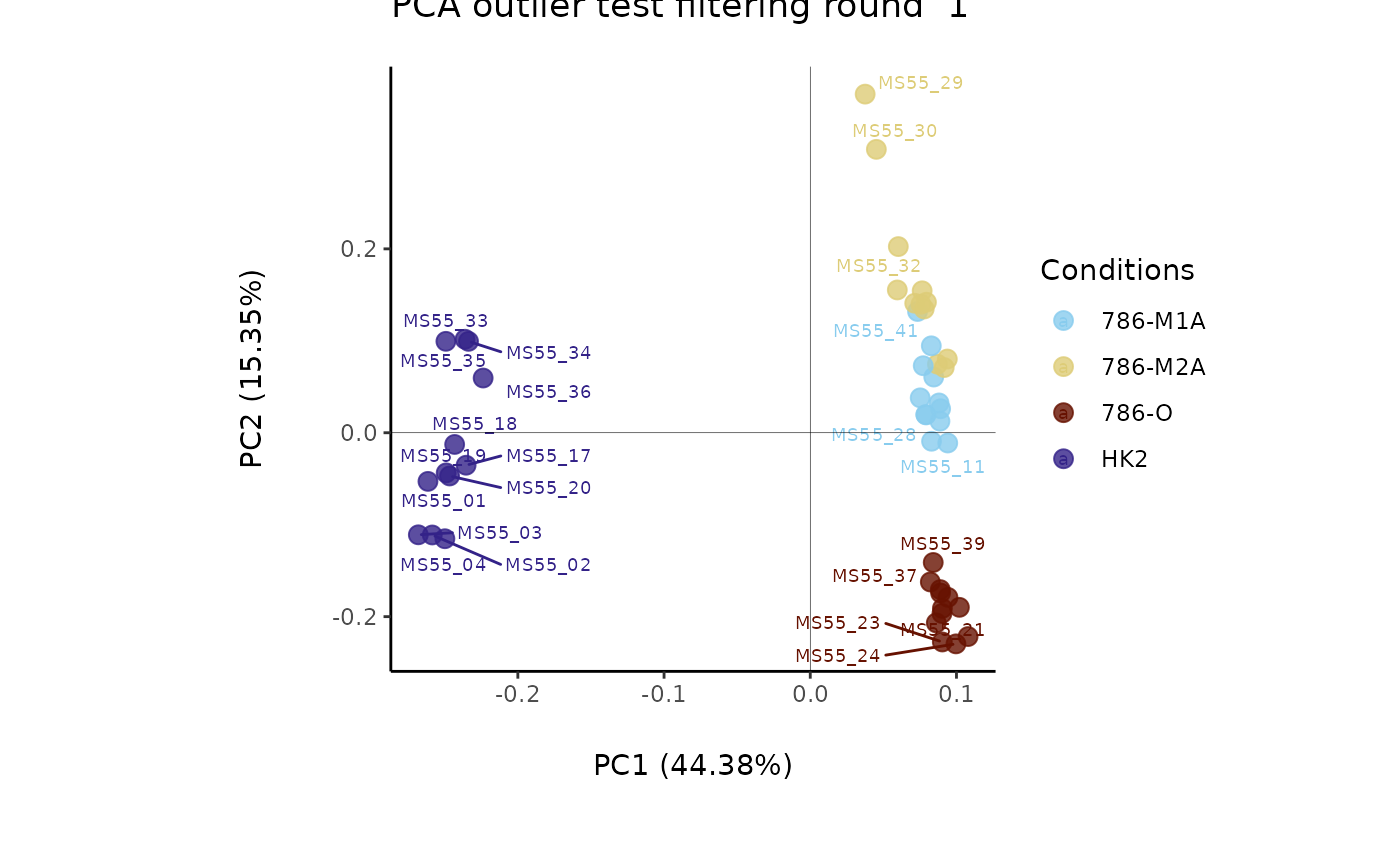
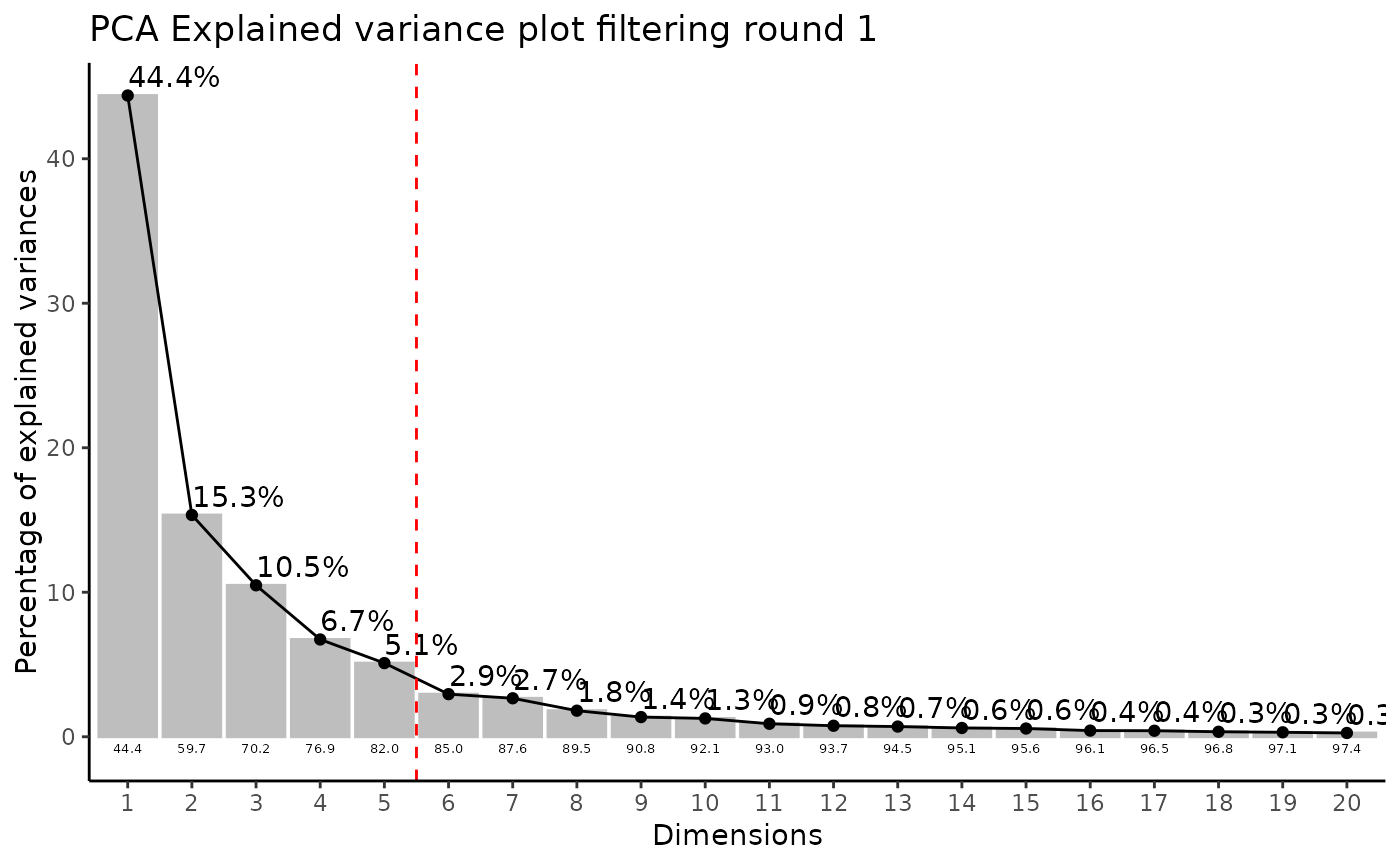
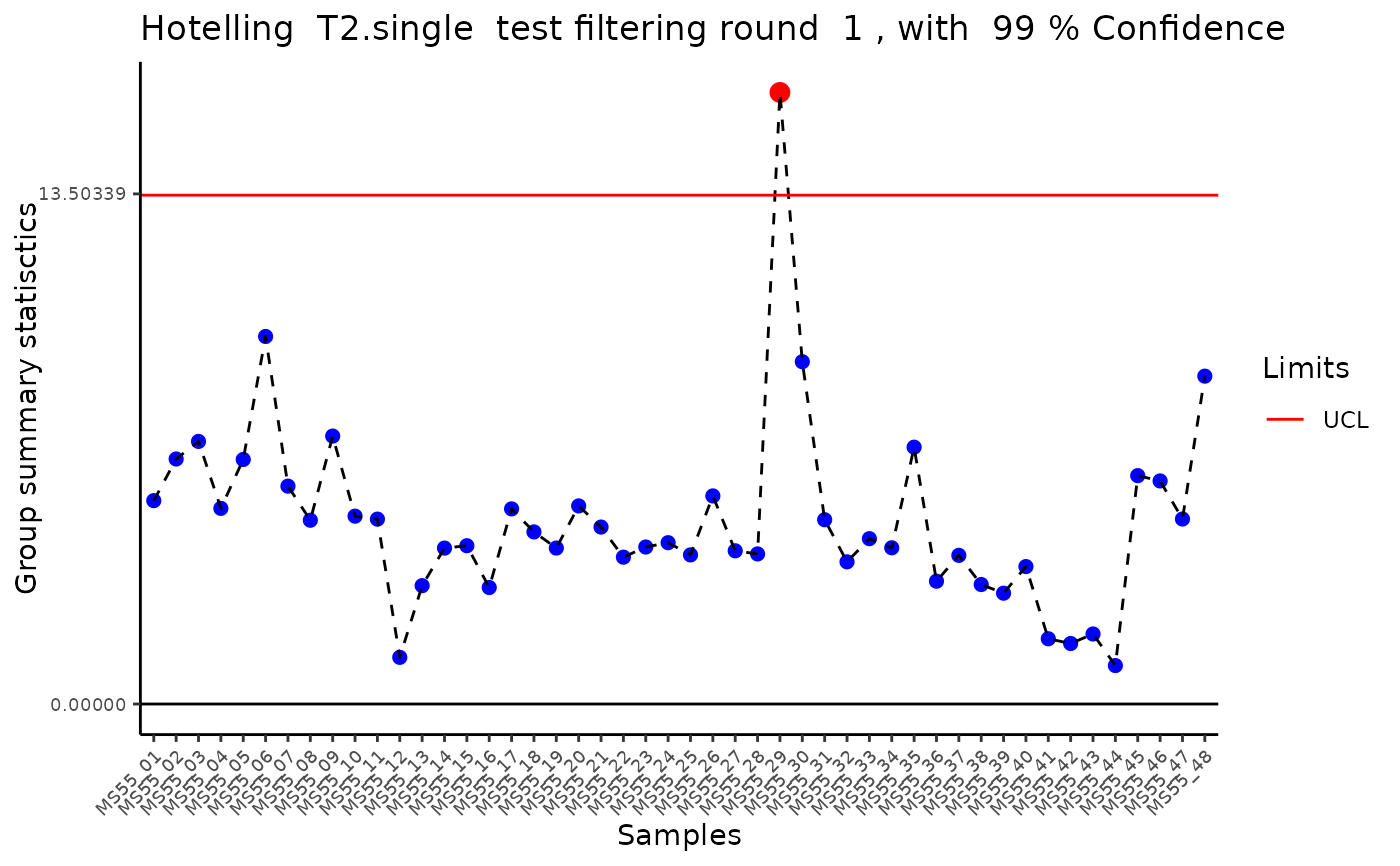
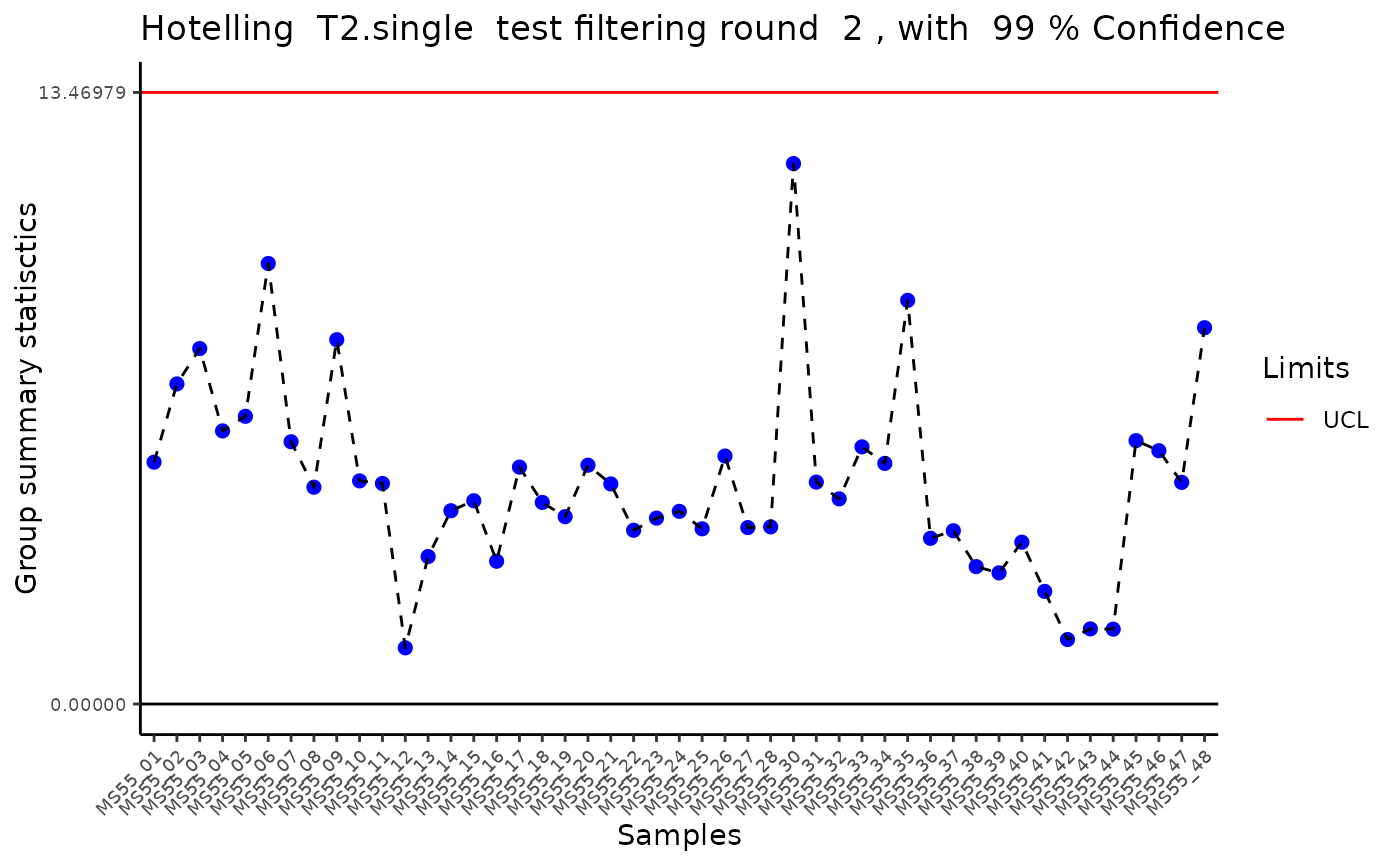
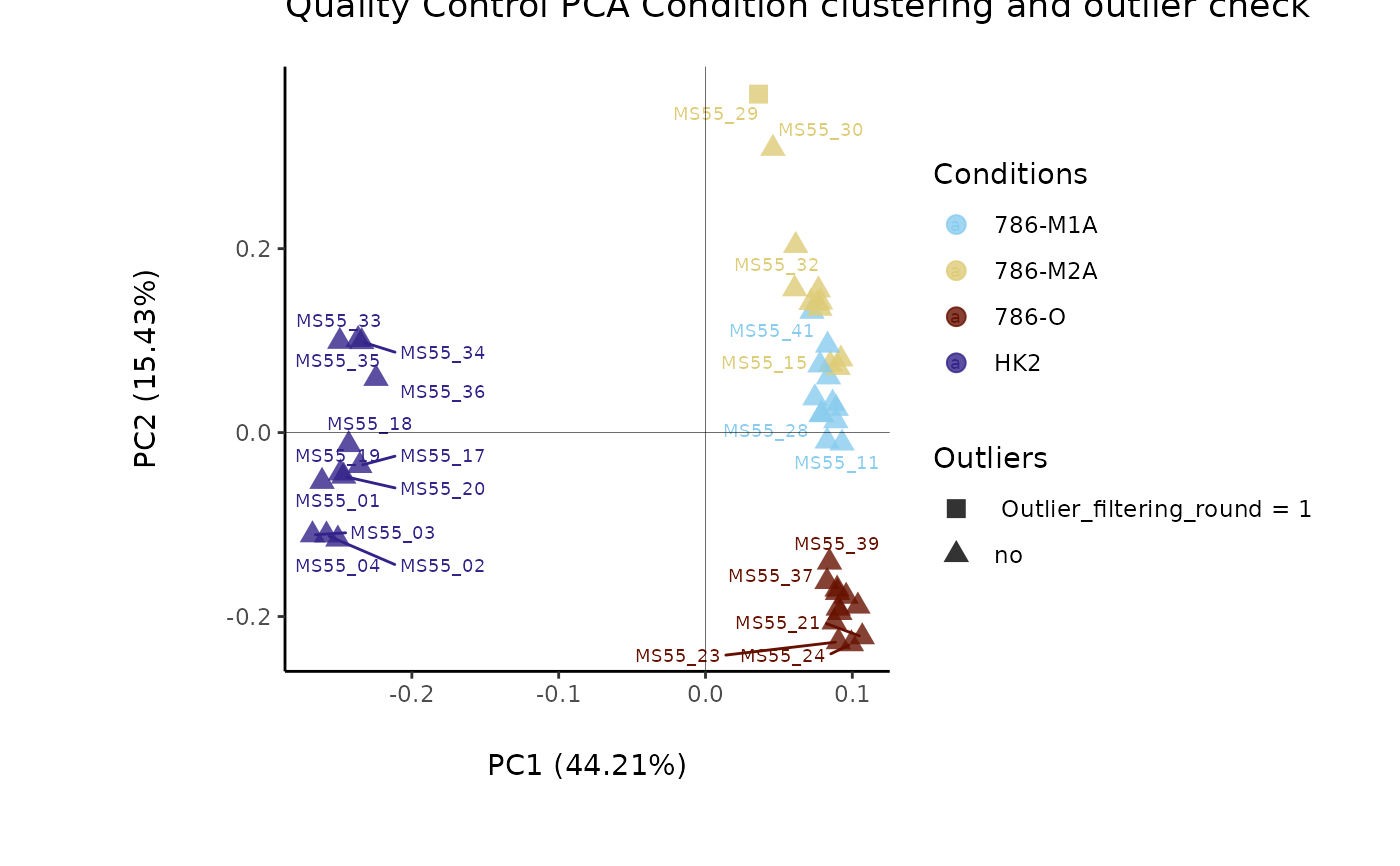
#> Outlier detection: Identification of outlier samples is performed using Hotellin's T2 test to define sample outliers in a mathematical way (Confidence = 0.99 ~ p.val < 0.01) (REF: Hotelling, H. (1931), Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 2 (3), 360-378, doi:https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177732979). hotellins_confidence value selected: 0.99
#> There are possible outlier samples in the data
#> Filtering round 1 Outlier Samples: MS55_29
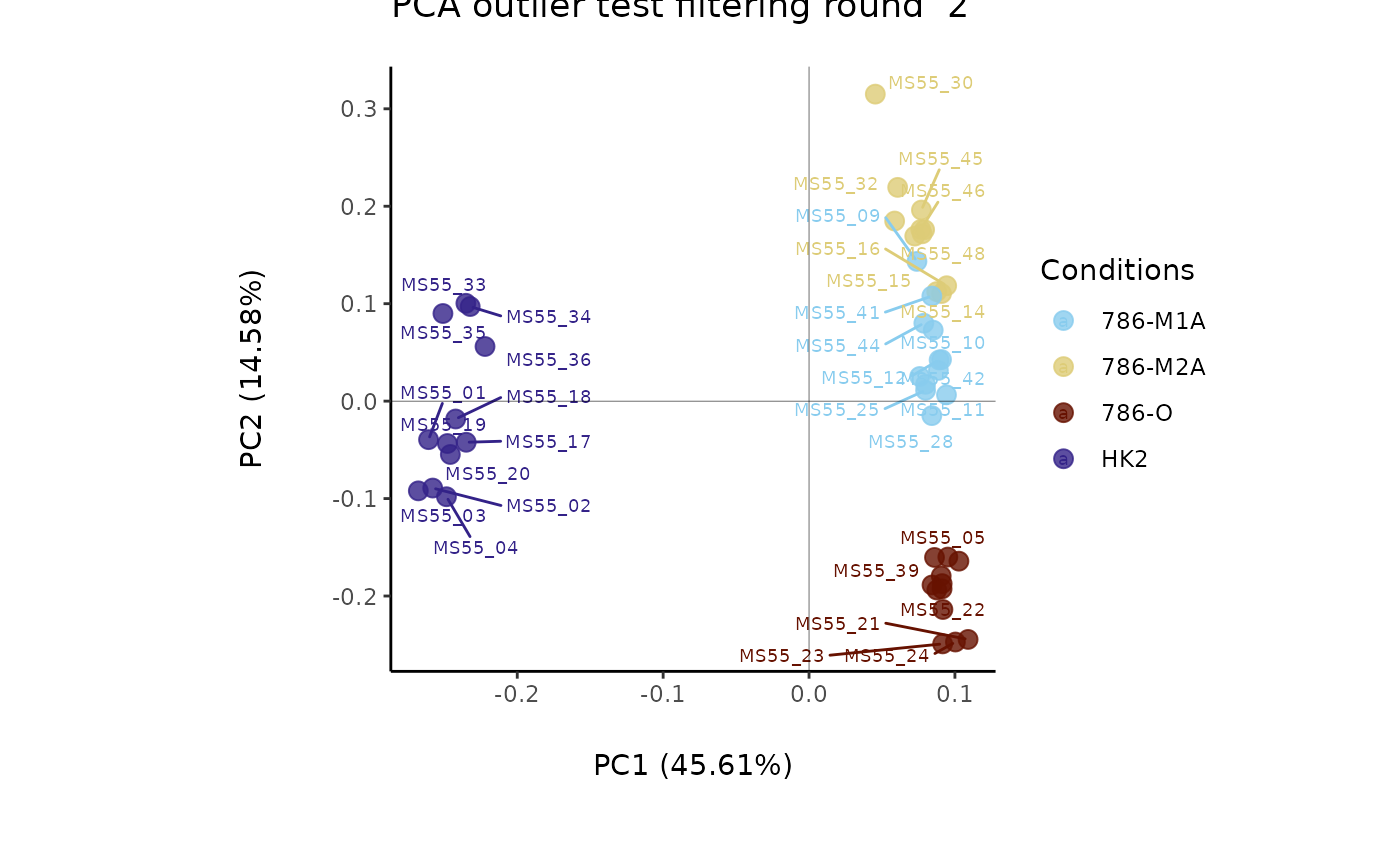
#> Filtering round 2 Outlier Samples: MS55_30
#> Warning: Removed 1 row containing missing values or values outside the scale range
#> (`geom_point()`).
#> Warning: Removed 1 row containing missing values or values outside the scale range
#> (`geom_point()`).
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 35 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 35 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 36 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 36 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 24 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 24 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 27 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 27 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 13 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 13 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 15 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 15 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 35 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 35 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 36 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 35 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 36 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 35 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 36 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 36 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 data(intracell_raw)
Intra <- intracell_raw %>% tibble::column_to_rownames("Code")
ResI <- processing(
data = Intra[-c(49:58), -c(1:3)],
metadata_sample = Intra[-c(49:58), c(1:3)],
metadata_info = c(
Conditions = "Conditions",
Biological_Replicates = "Biological_Replicates"
)
)
#> feature_filtering: Here we apply the modified 80%-filtering rule that takes the class information (Column `Conditions`) into account, which additionally reduces the effect of missing values (REF: Yang et. al., (2015), doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00004). Filtering value selected: 0.8
#> 3 metabolites where removed: AICAR, FAICAR, SAICAR
#> Missing Value Imputation: Missing value imputation is performed, as a complementary approach to address the missing value problem, where the missing values are imputing using the `half minimum value`. REF: Wei et. al., (2018), Reports, 8, 663, doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-19120-0
#> total Ion Count (tic) normalization: total Ion Count (tic) normalization is used to reduce the variation from non-biological sources, while maintaining the biological variation. REF: Wulff et. al., (2018), Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 9, 339-351, doi:https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2018.98022
#> Outlier detection: Identification of outlier samples is performed using Hotellin's T2 test to define sample outliers in a mathematical way (Confidence = 0.99 ~ p.val < 0.01) (REF: Hotelling, H. (1931), Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 2 (3), 360-378, doi:https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177732979). hotellins_confidence value selected: 0.99
#> There are possible outlier samples in the data
#> Filtering round 1 Outlier Samples: MS55_29
data(intracell_raw)
Intra <- intracell_raw %>% tibble::column_to_rownames("Code")
ResI <- processing(
data = Intra[-c(49:58), -c(1:3)],
metadata_sample = Intra[-c(49:58), c(1:3)],
metadata_info = c(
Conditions = "Conditions",
Biological_Replicates = "Biological_Replicates"
)
)
#> feature_filtering: Here we apply the modified 80%-filtering rule that takes the class information (Column `Conditions`) into account, which additionally reduces the effect of missing values (REF: Yang et. al., (2015), doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00004). Filtering value selected: 0.8
#> 3 metabolites where removed: AICAR, FAICAR, SAICAR
#> Missing Value Imputation: Missing value imputation is performed, as a complementary approach to address the missing value problem, where the missing values are imputing using the `half minimum value`. REF: Wei et. al., (2018), Reports, 8, 663, doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-19120-0
#> total Ion Count (tic) normalization: total Ion Count (tic) normalization is used to reduce the variation from non-biological sources, while maintaining the biological variation. REF: Wulff et. al., (2018), Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 9, 339-351, doi:https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2018.98022
#> Outlier detection: Identification of outlier samples is performed using Hotellin's T2 test to define sample outliers in a mathematical way (Confidence = 0.99 ~ p.val < 0.01) (REF: Hotelling, H. (1931), Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 2 (3), 360-378, doi:https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177732979). hotellins_confidence value selected: 0.99
#> There are possible outlier samples in the data
#> Filtering round 1 Outlier Samples: MS55_29
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 16 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 16 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 16 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 16 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
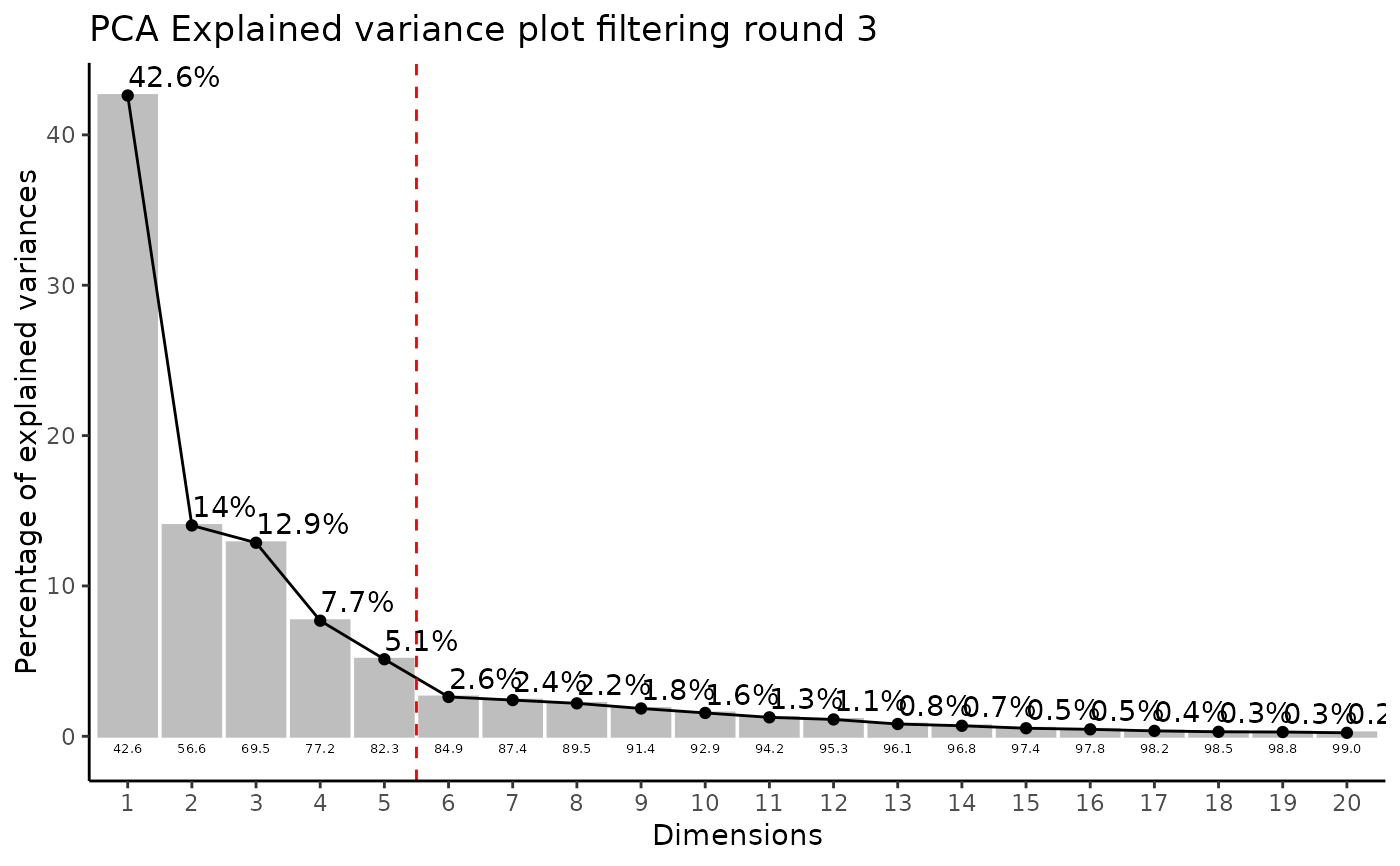 #> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
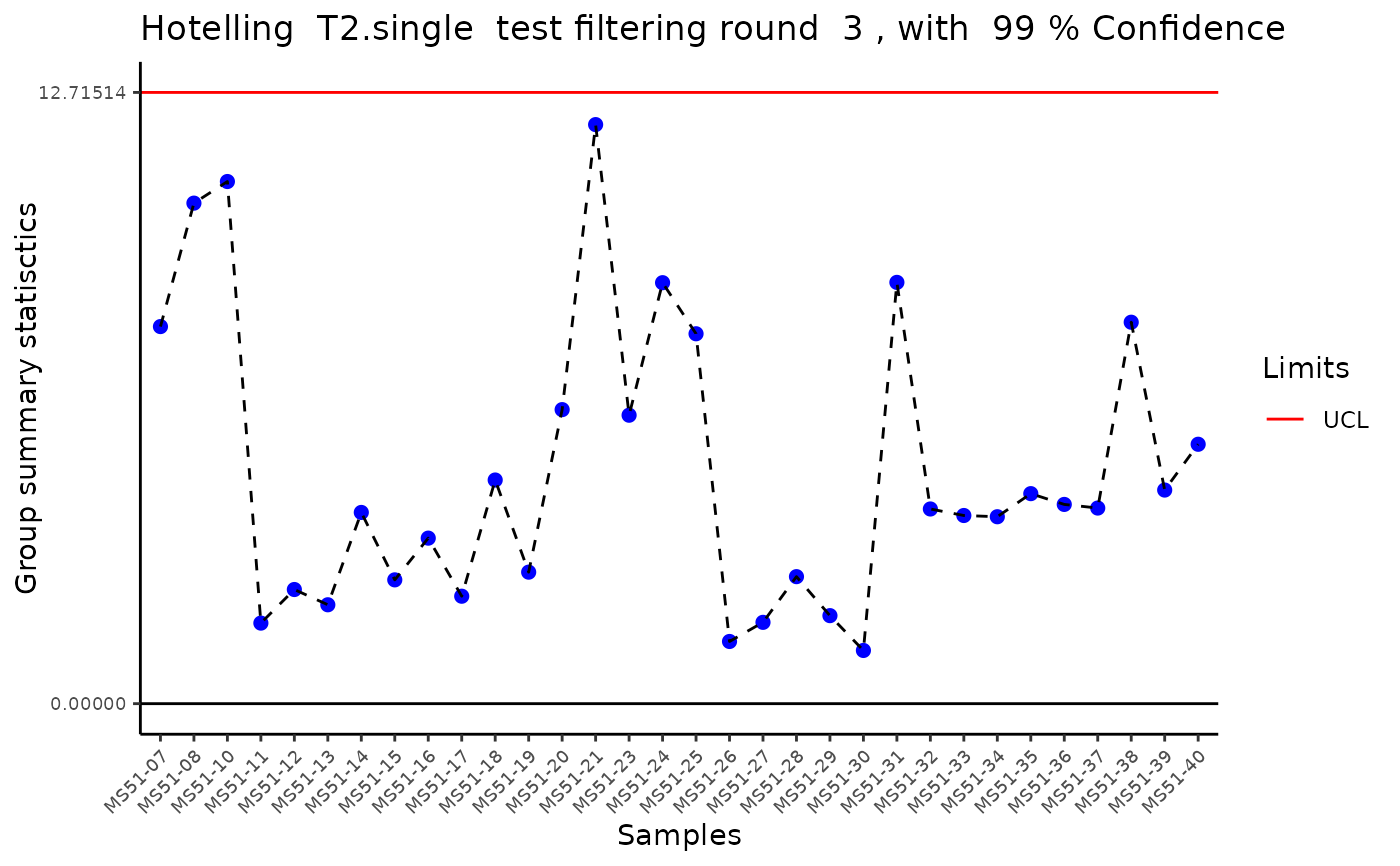 #> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
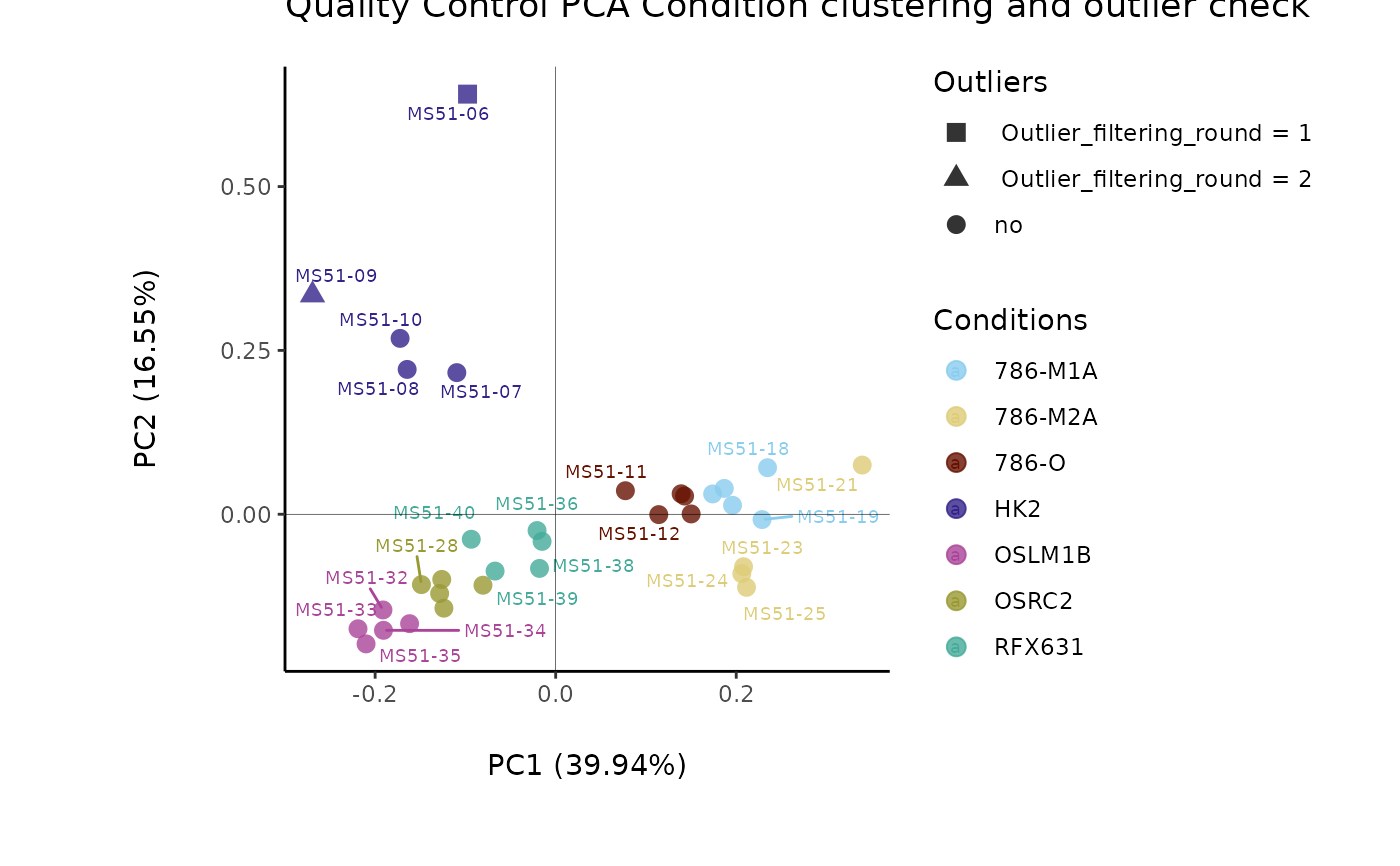 #> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 26 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
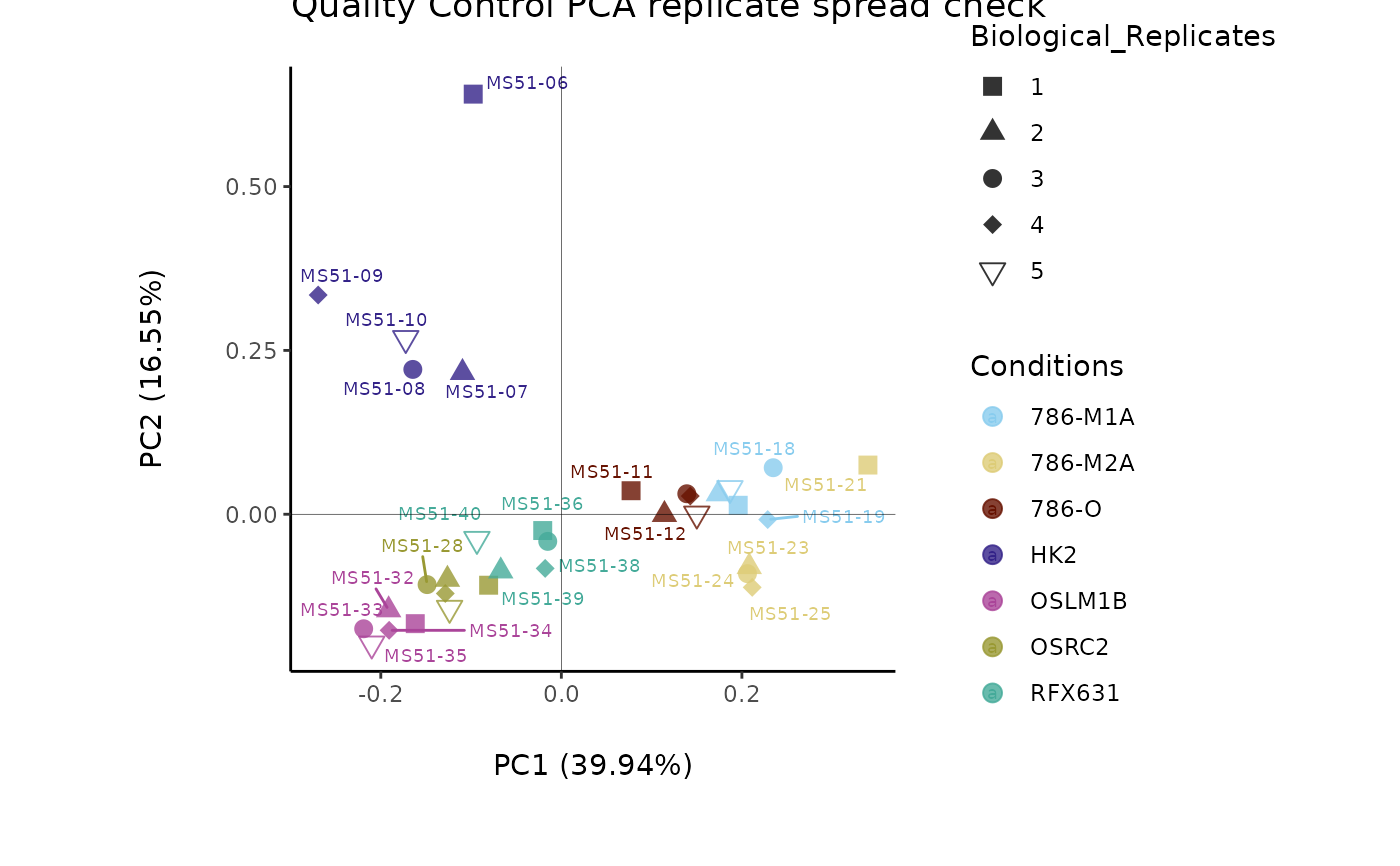 data(medium_raw)
Media <- medium_raw %>% tibble::column_to_rownames("Code")
ResM <- processing(
data = Media[-c(40:45), -c(1:3)],
metadata_sample = Media[-c(40:45), c(1:3)],
metadata_info = c(
Conditions = "Conditions",
Biological_Replicates = "Biological_Replicates",
core_norm_factor = "GrowthFactor",
core_media = "blank"
),
core = TRUE
)
#> For Consumption Release experiment we are using the method from Jain M. REF: Jain et. al, (2012), Science 336(6084):1040-4, doi: 10.1126/science.1218595.
#> feature_filtering: Here we apply the modified 80%-filtering rule that takes the class information (Column `Conditions`) into account, which additionally reduces the effect of missing values (REF: Yang et. al., (2015), doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00004). Filtering value selected: 0.8
#> 3 metabolites where removed: N-acetylaspartylglutamate, hypotaurine, S-(2-succinyl)cysteine
#> Missing Value Imputation: Missing value imputation is performed, as a complementary approach to address the missing value problem, where the missing values are imputing using the `half minimum value`. REF: Wei et. al., (2018), Reports, 8, 663, doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-19120-0
#> NA values were found in Control_media samples for metabolites. For metabolites including NAs mvi is performed unless all samples of a metabolite are NA.
#> Metabolites with high NA load (>20%) in Control_media samples are: dihydroorotate.
#> Metabolites with only NAs (= 100%) in Control_media samples are: hydroxyphenylpyruvate. Those NAs are set zero as we consider them true zeros
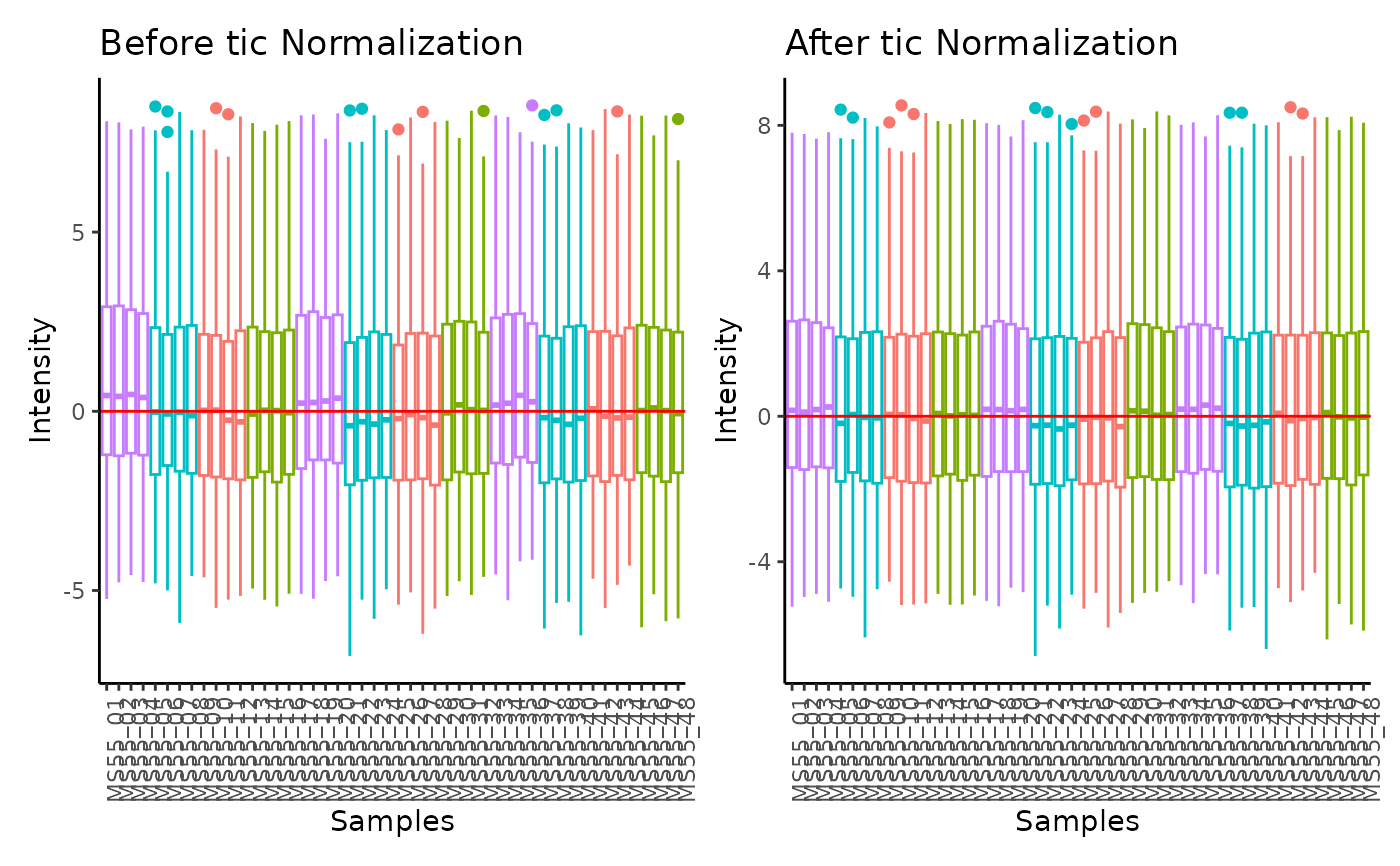
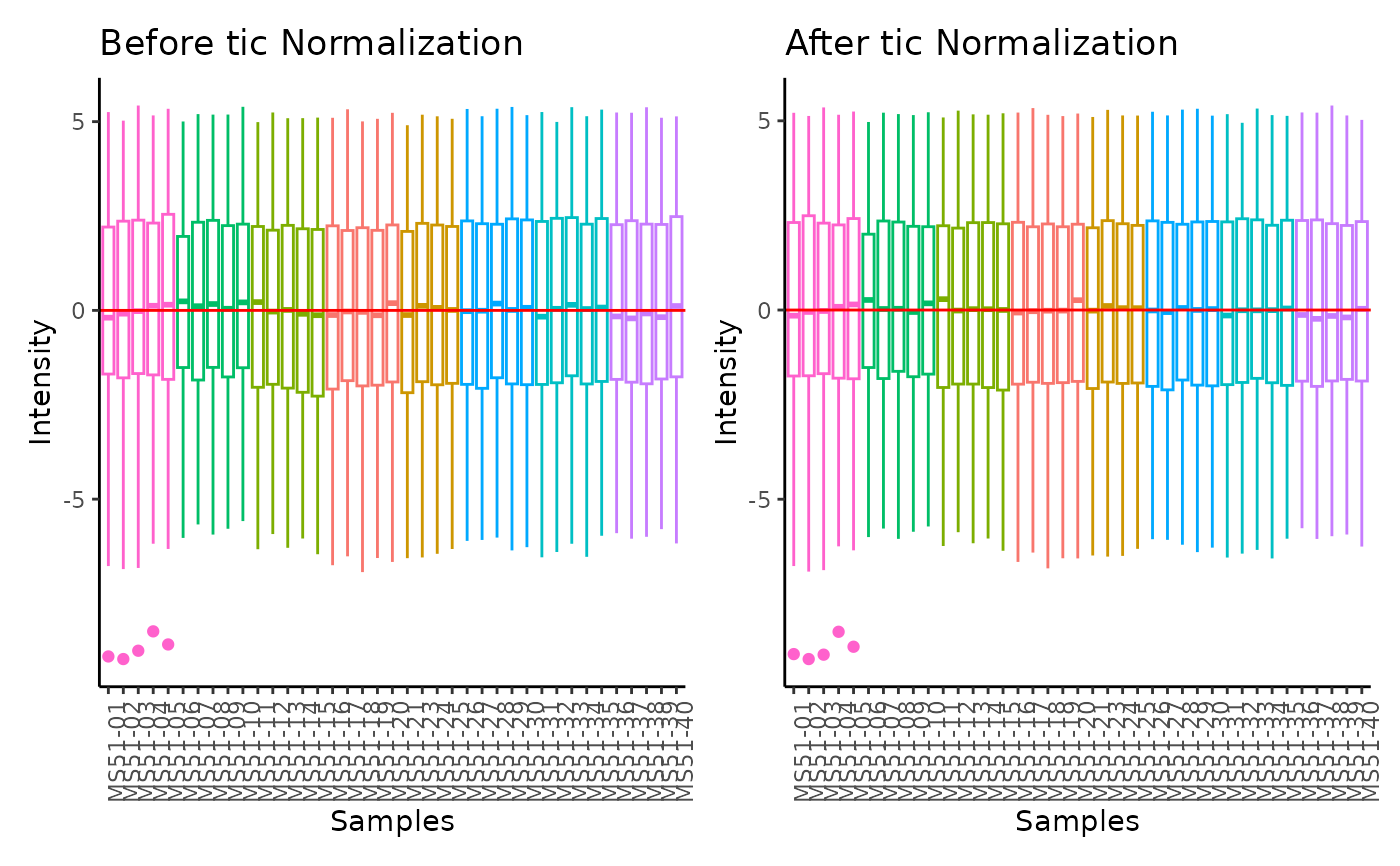
#> total Ion Count (tic) normalization: total Ion Count (tic) normalization is used to reduce the variation from non-biological sources, while maintaining the biological variation. REF: Wulff et. al., (2018), Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 9, 339-351, doi:https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2018.98022
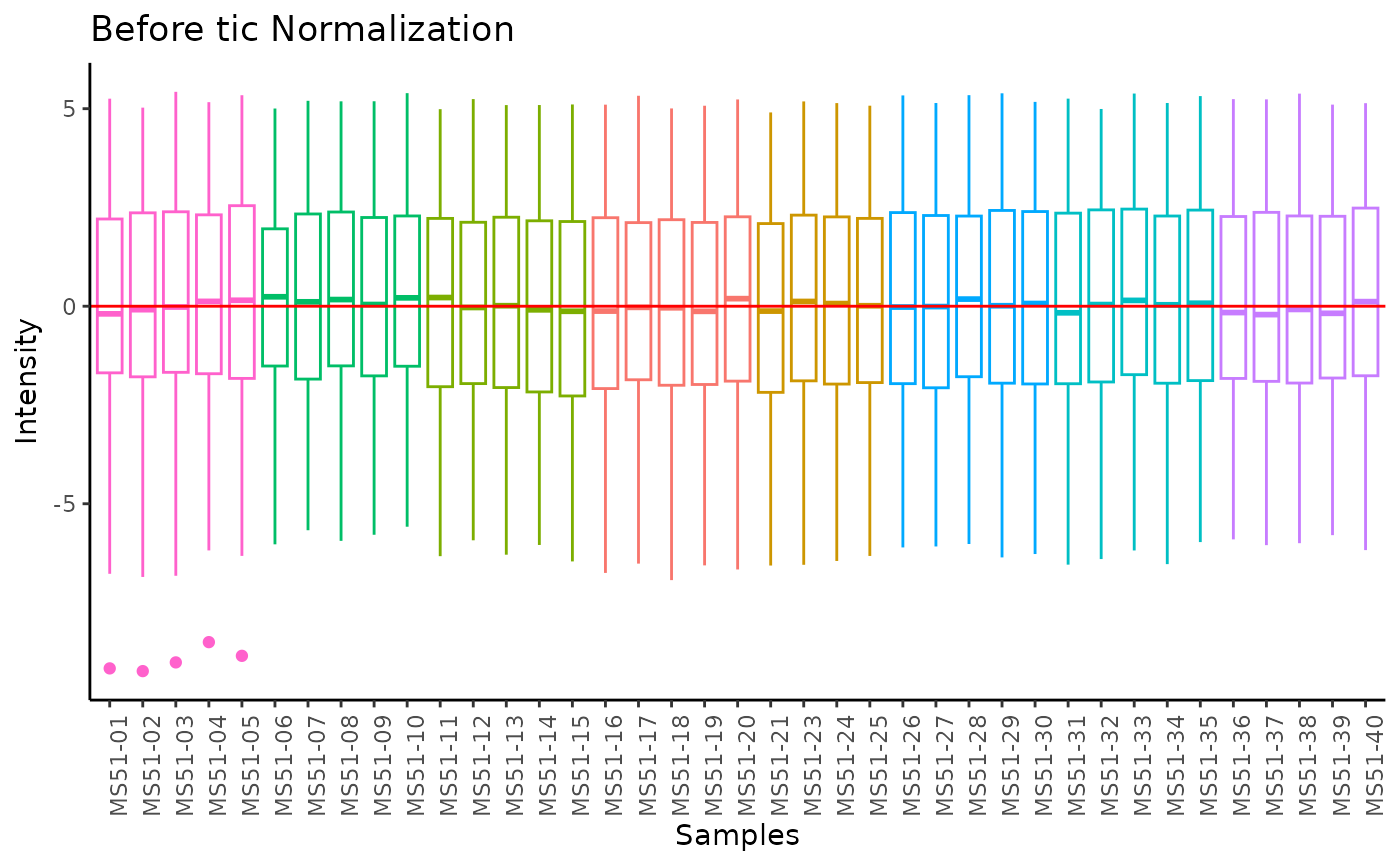
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
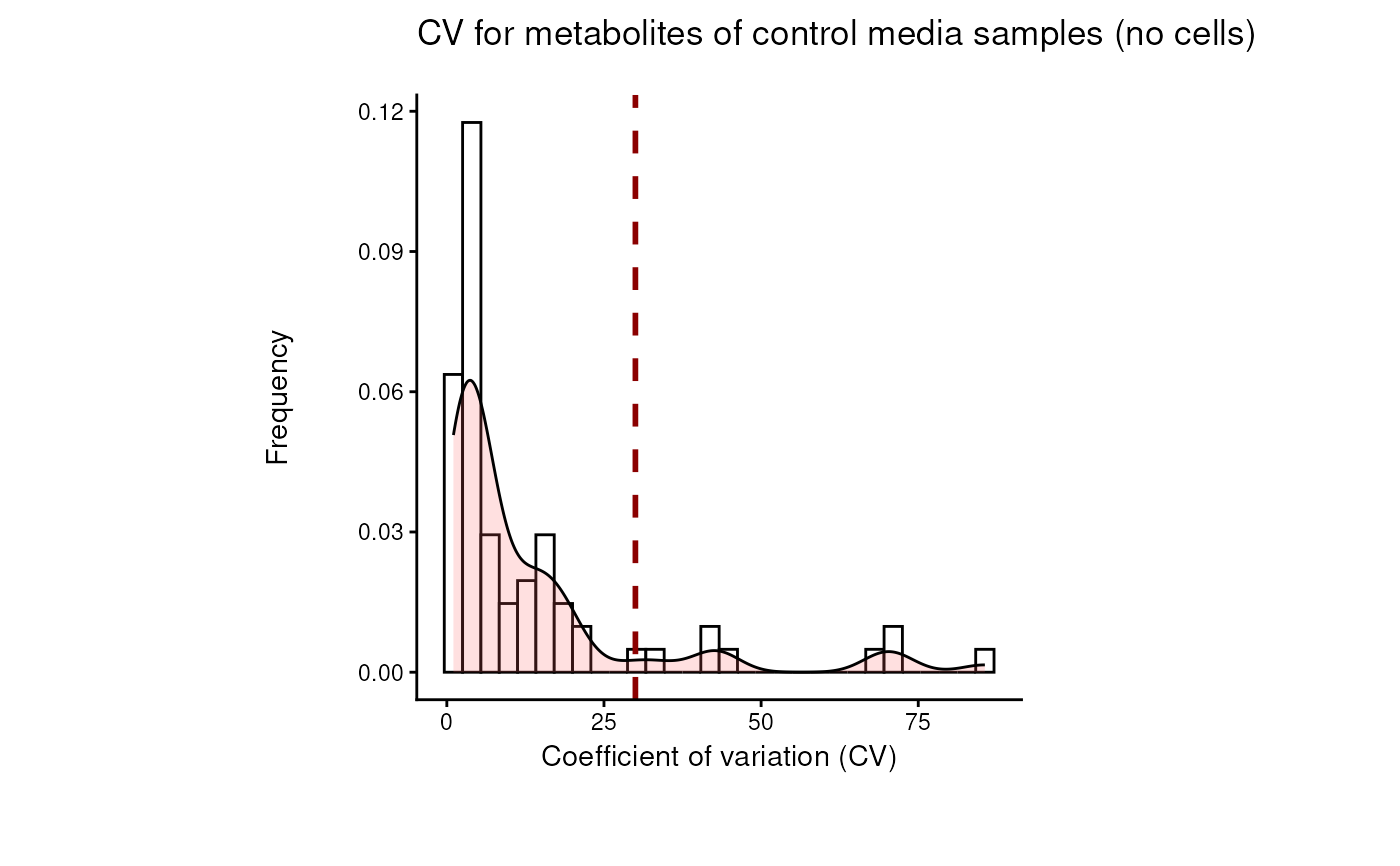
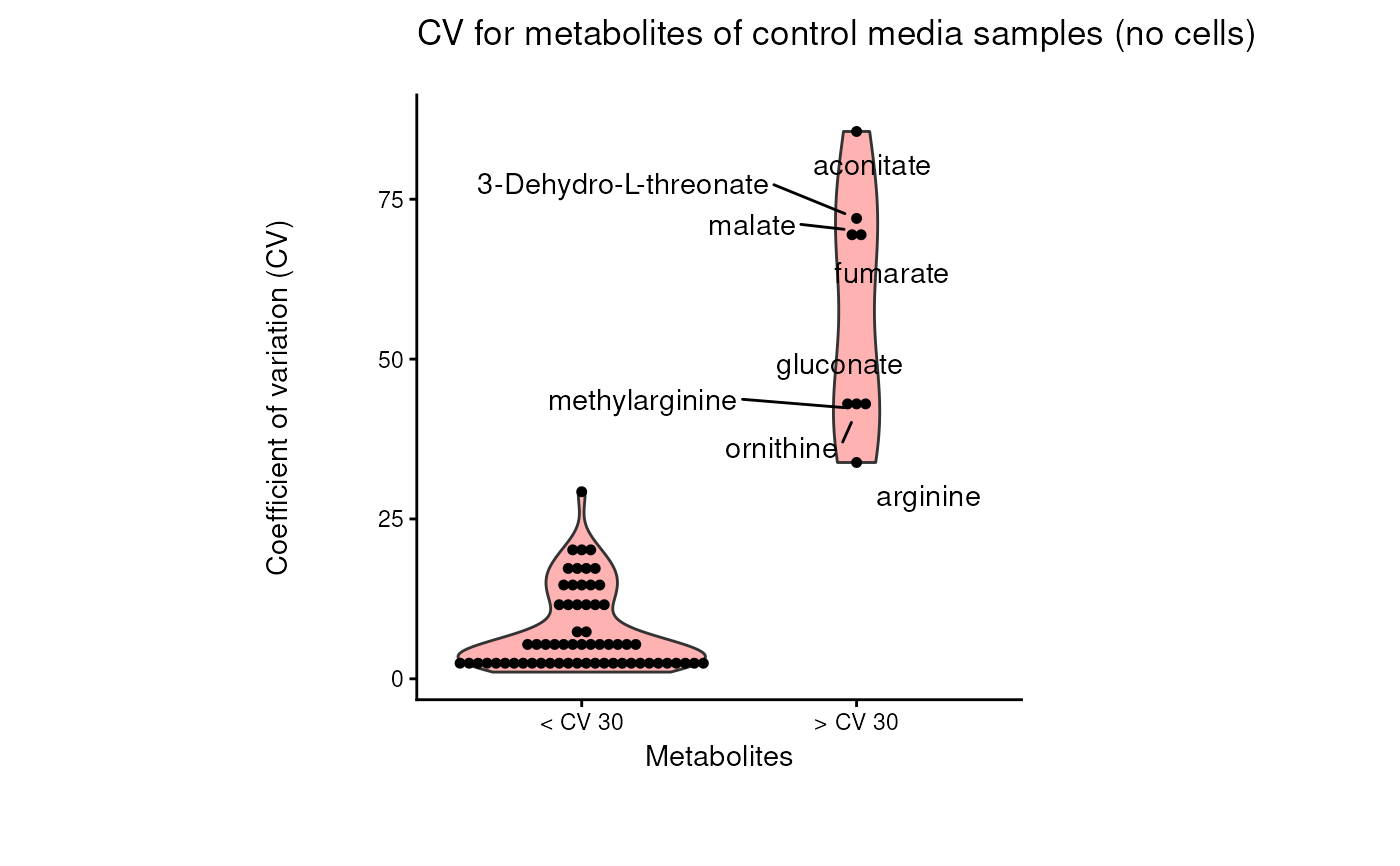
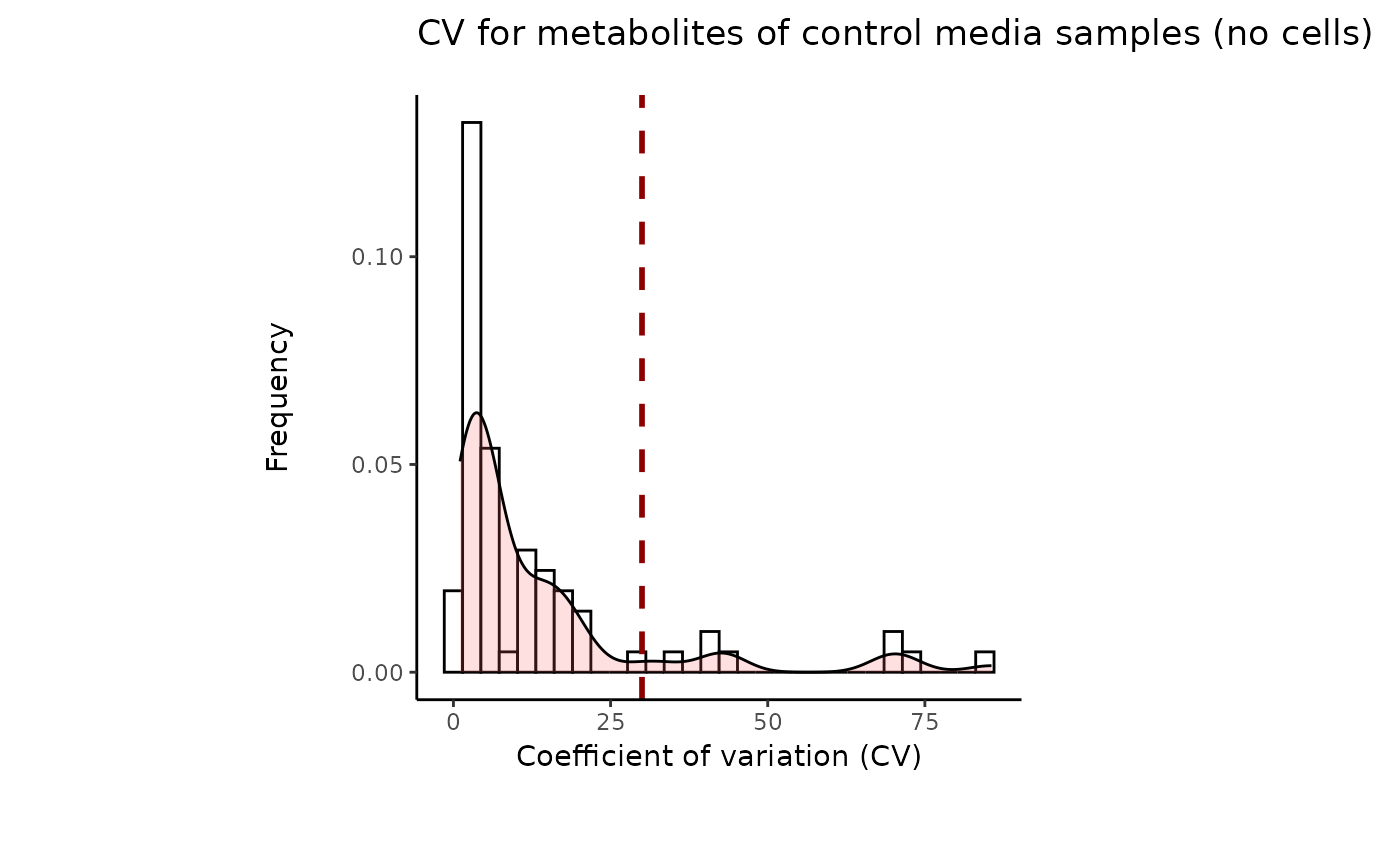
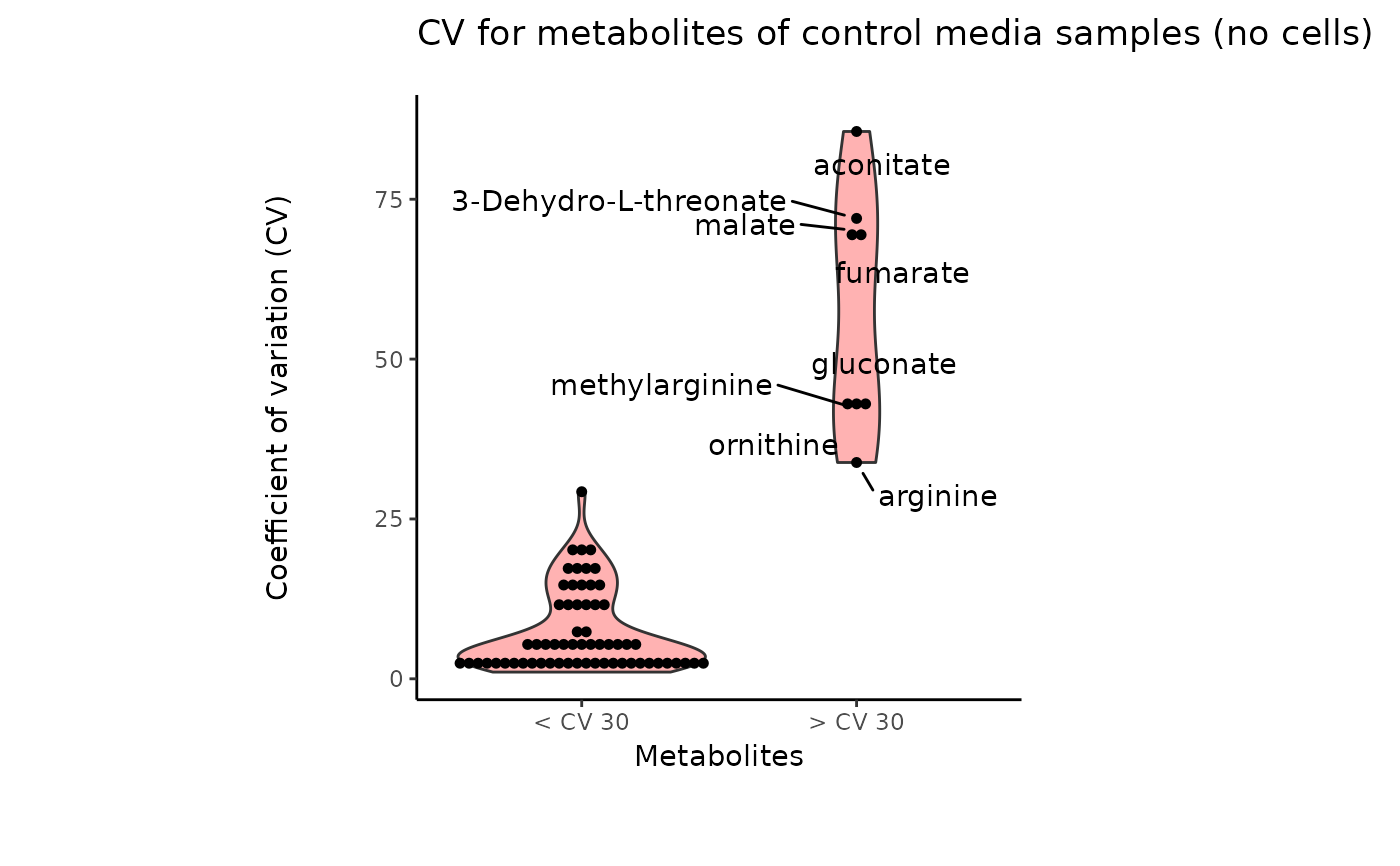
#> 8 of variables have high variability (CV > 30) in the core_media control samples. Consider checking the pooled samples to decide whether to remove these metabolites or not.
#> `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value `binwidth`.
#> Warning: The following aesthetics were dropped during statistical transformation: label.
#> ℹ This can happen when ggplot fails to infer the correct grouping structure in
#> the data.
#> ℹ Did you forget to specify a `group` aesthetic or to convert a numerical
#> variable into a factor?
#> Bin width defaults to 1/30 of the range of the data. Pick better value with
#> `binwidth`.
#> Warning: The following aesthetics were dropped during statistical transformation: label.
#> ℹ This can happen when ggplot fails to infer the correct grouping structure in
#> the data.
#> ℹ Did you forget to specify a `group` aesthetic or to convert a numerical
#> variable into a factor?
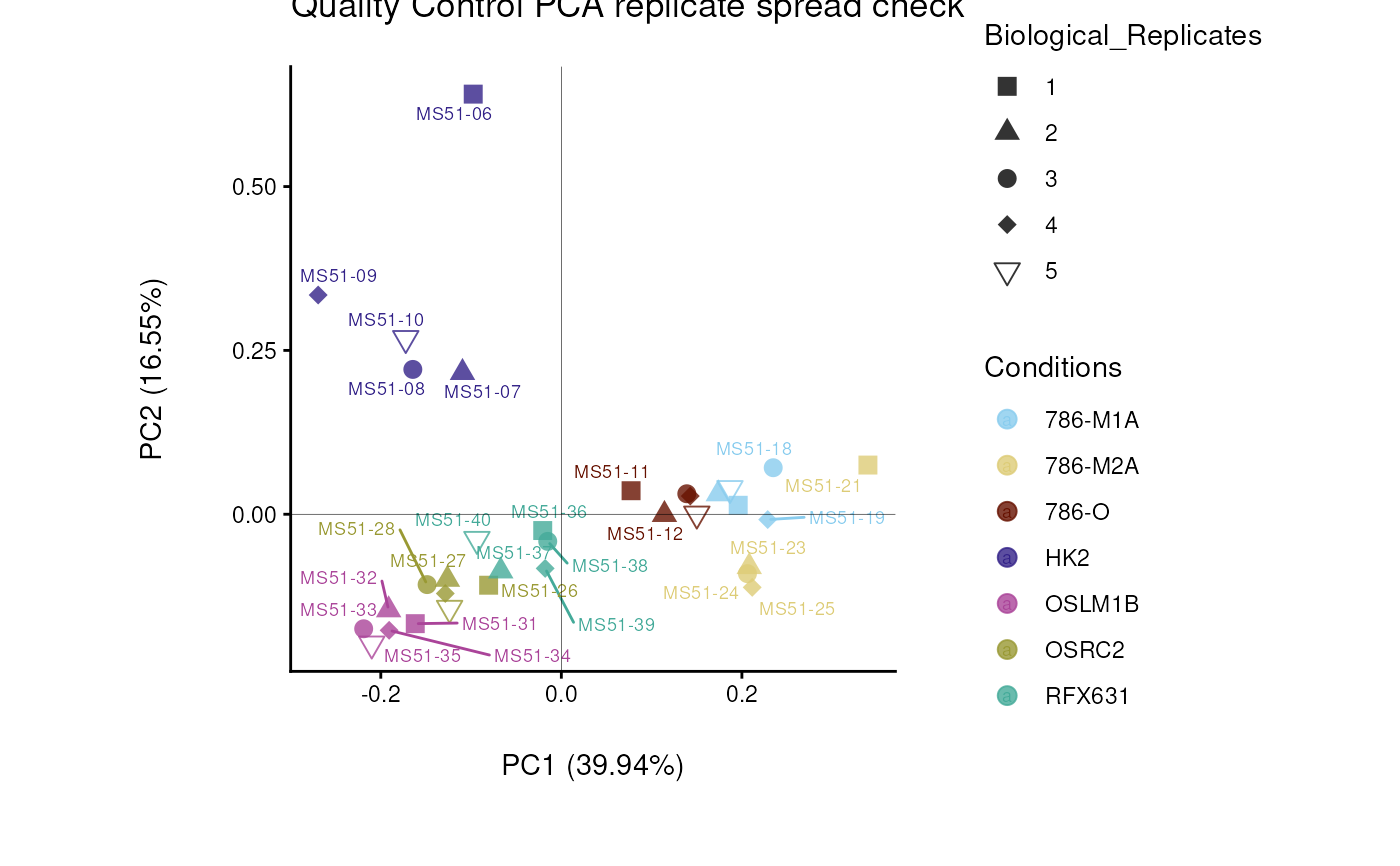
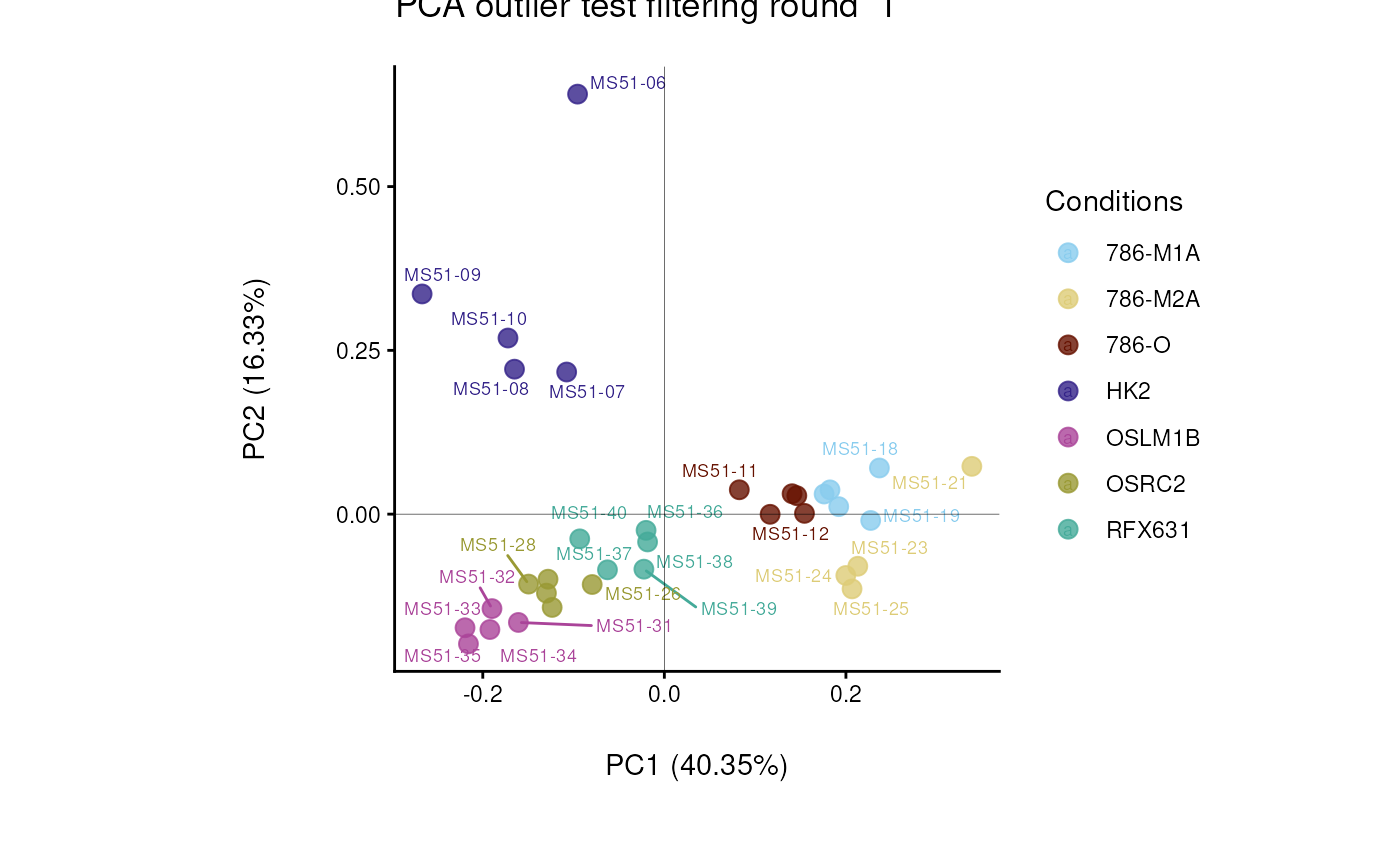
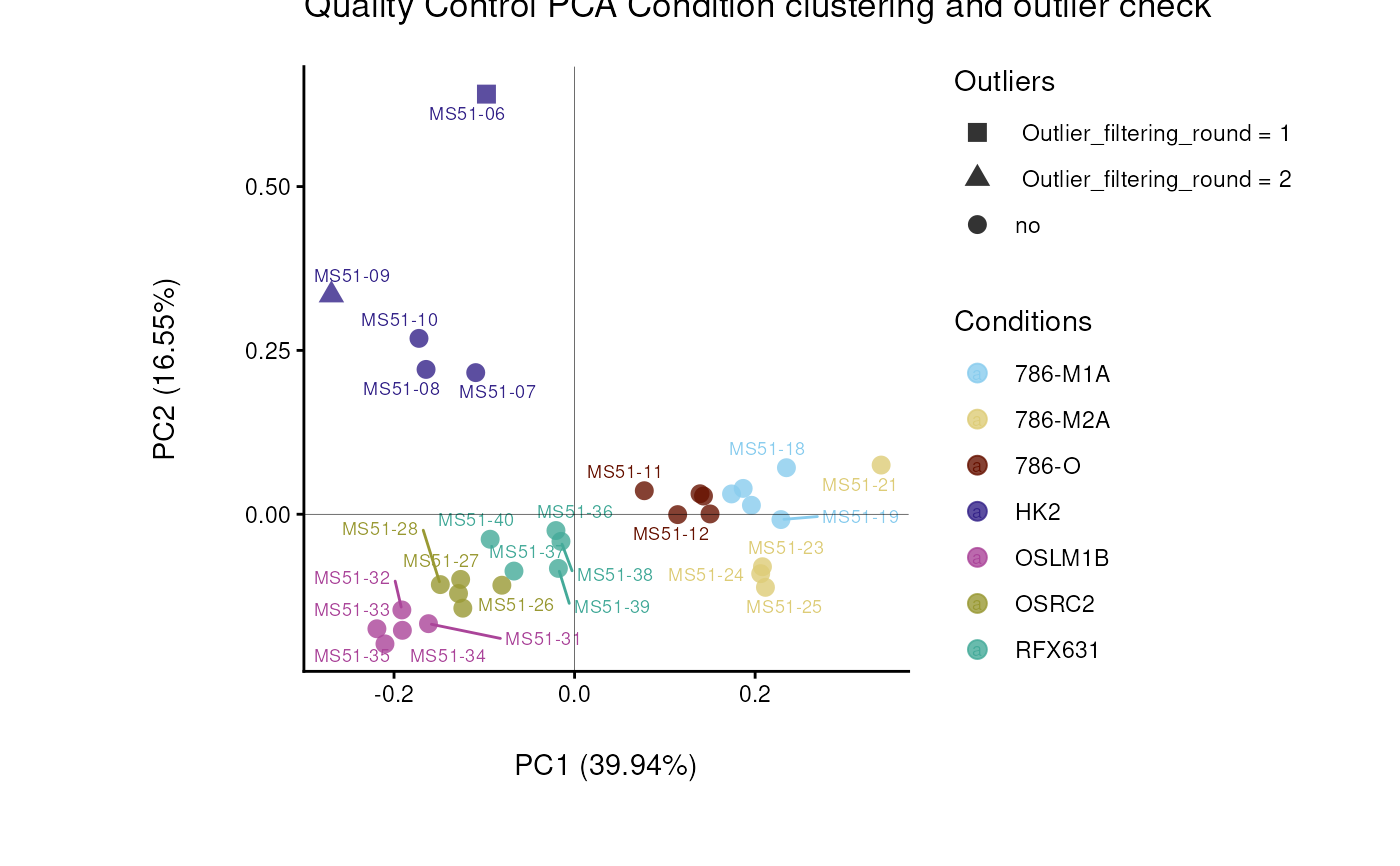
#> Warning: The core_media samples MS51-06 were found to be different from the rest. They will not be included in the sum of the core_media samples.
#> core data are normalised by substracting mean (blank) from each sample and multiplying with the core_norm_factor
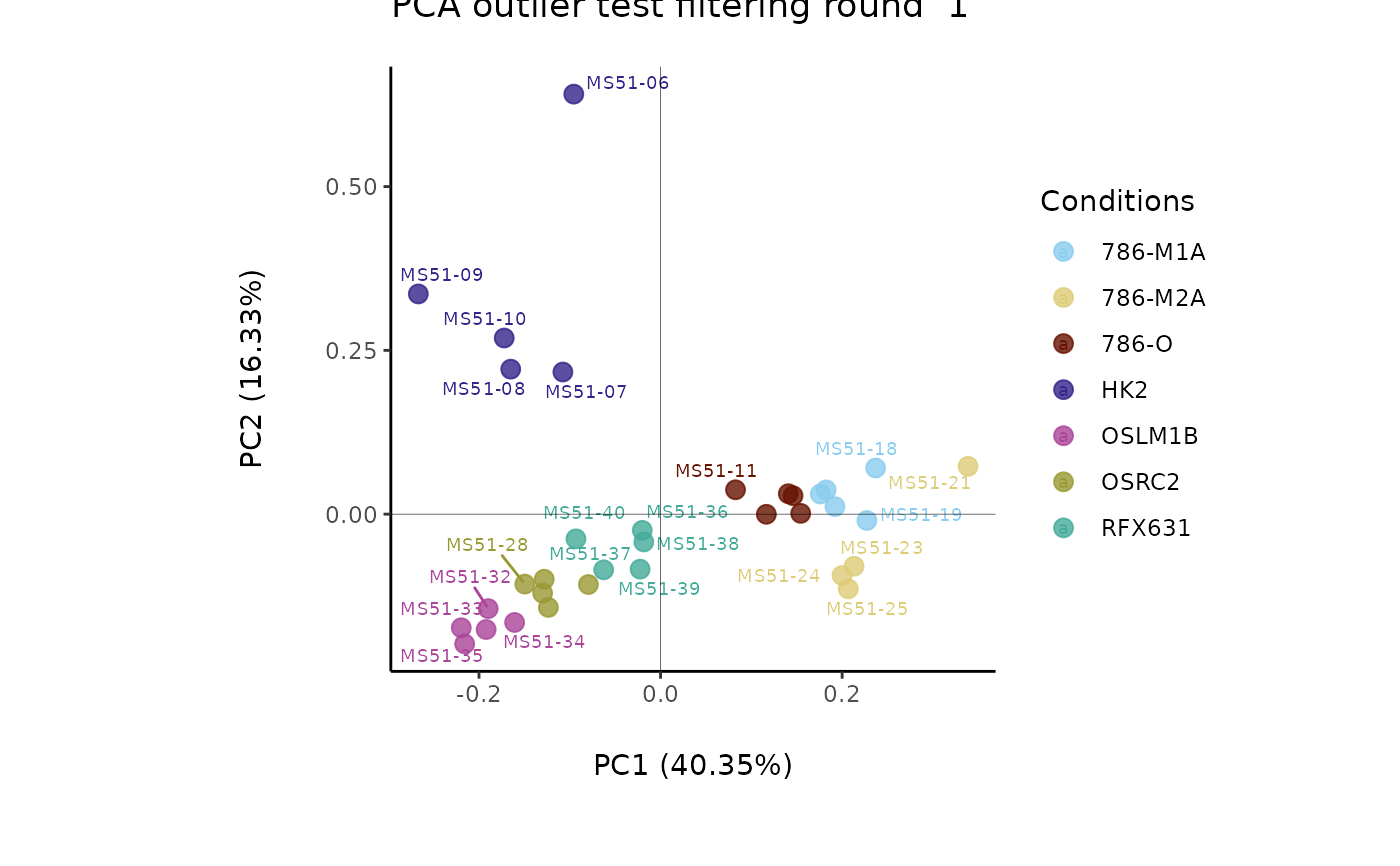
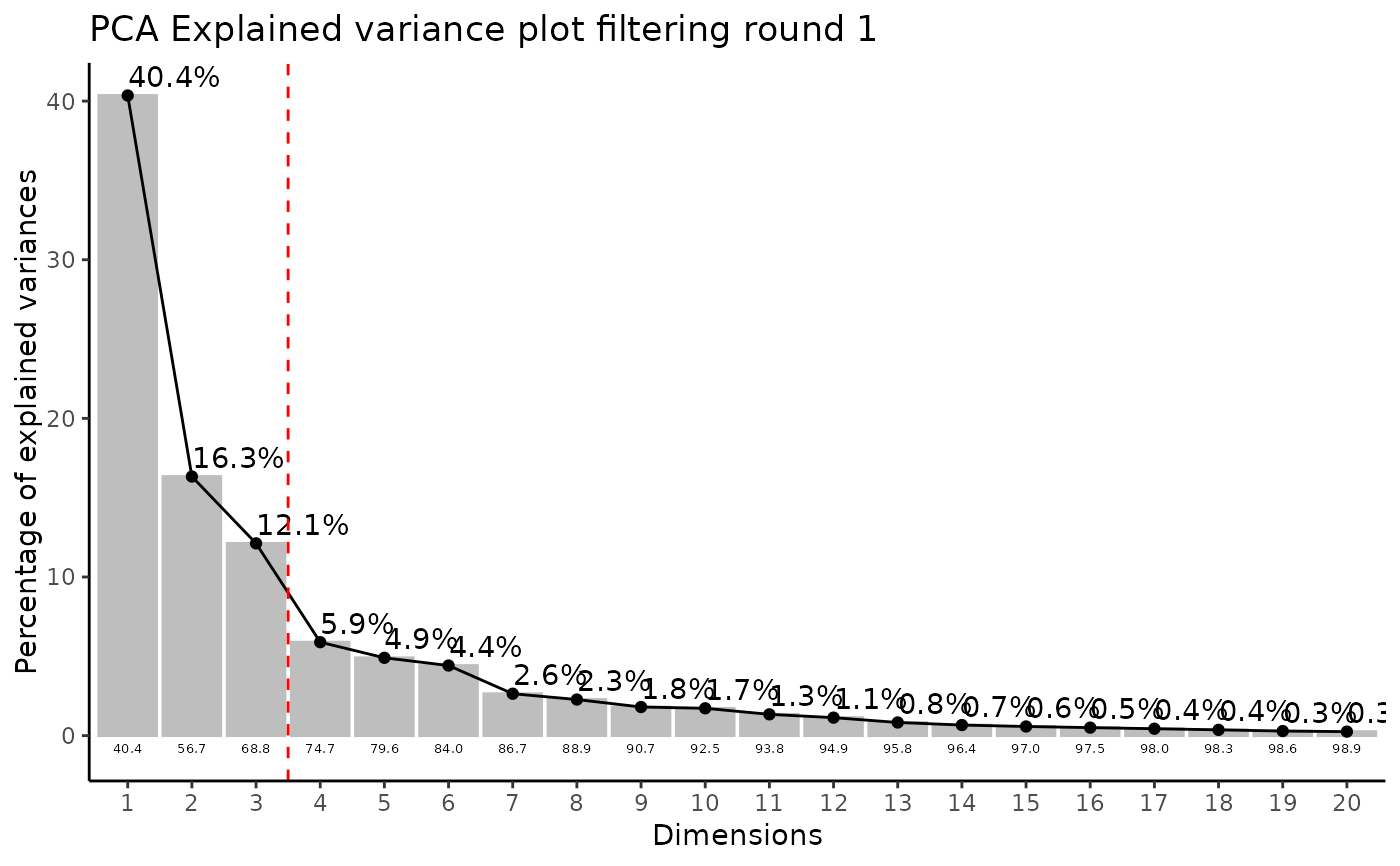
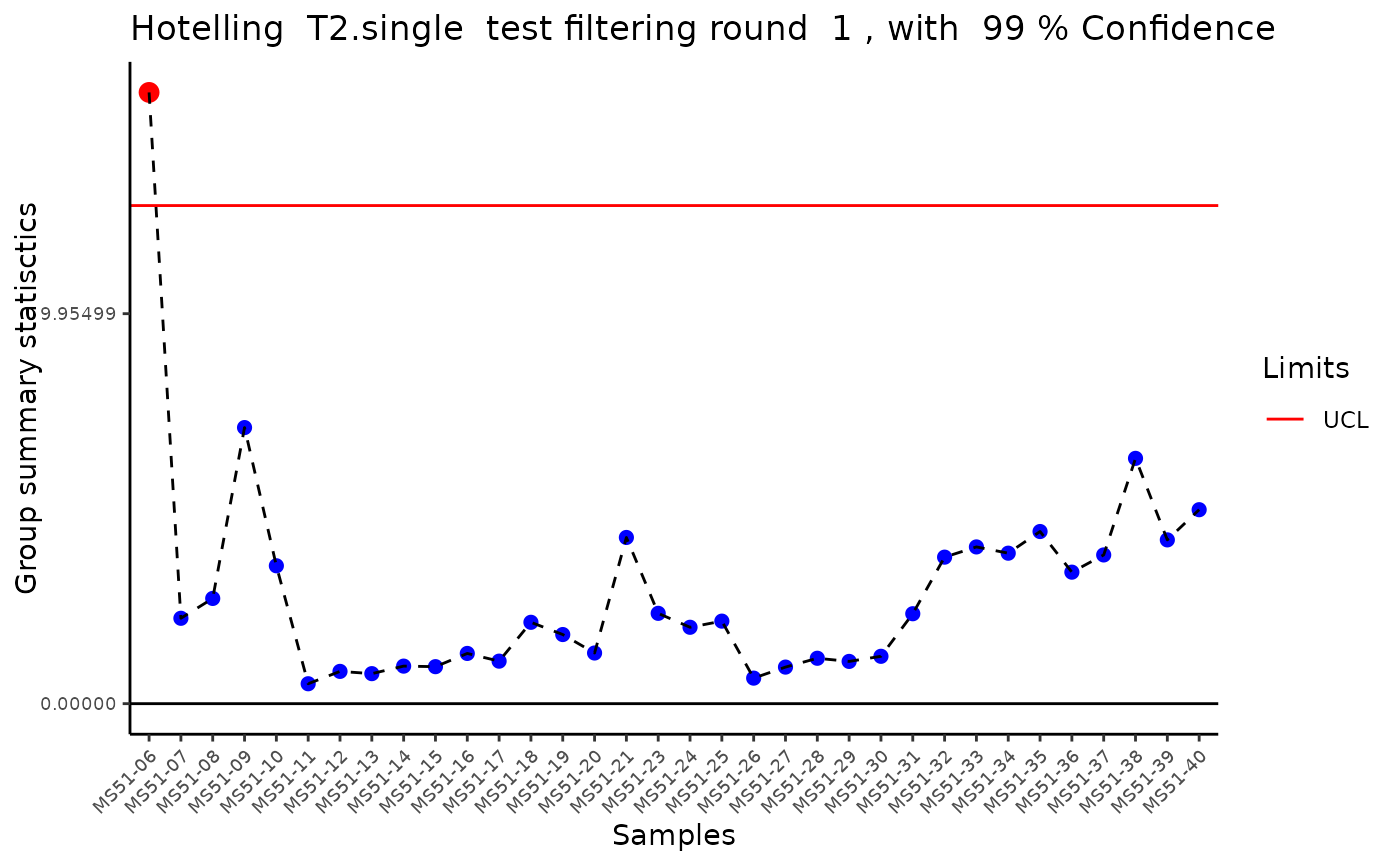
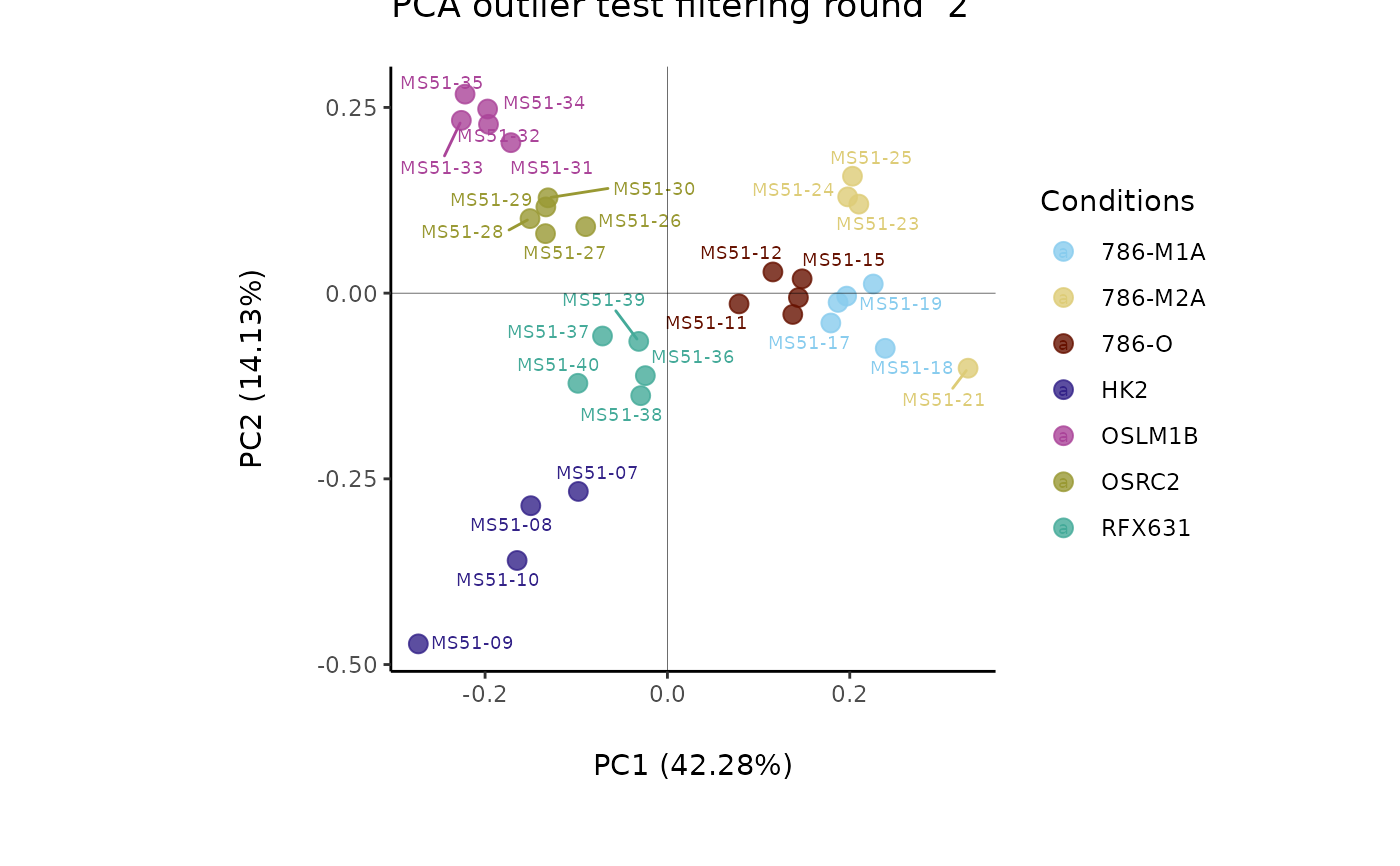
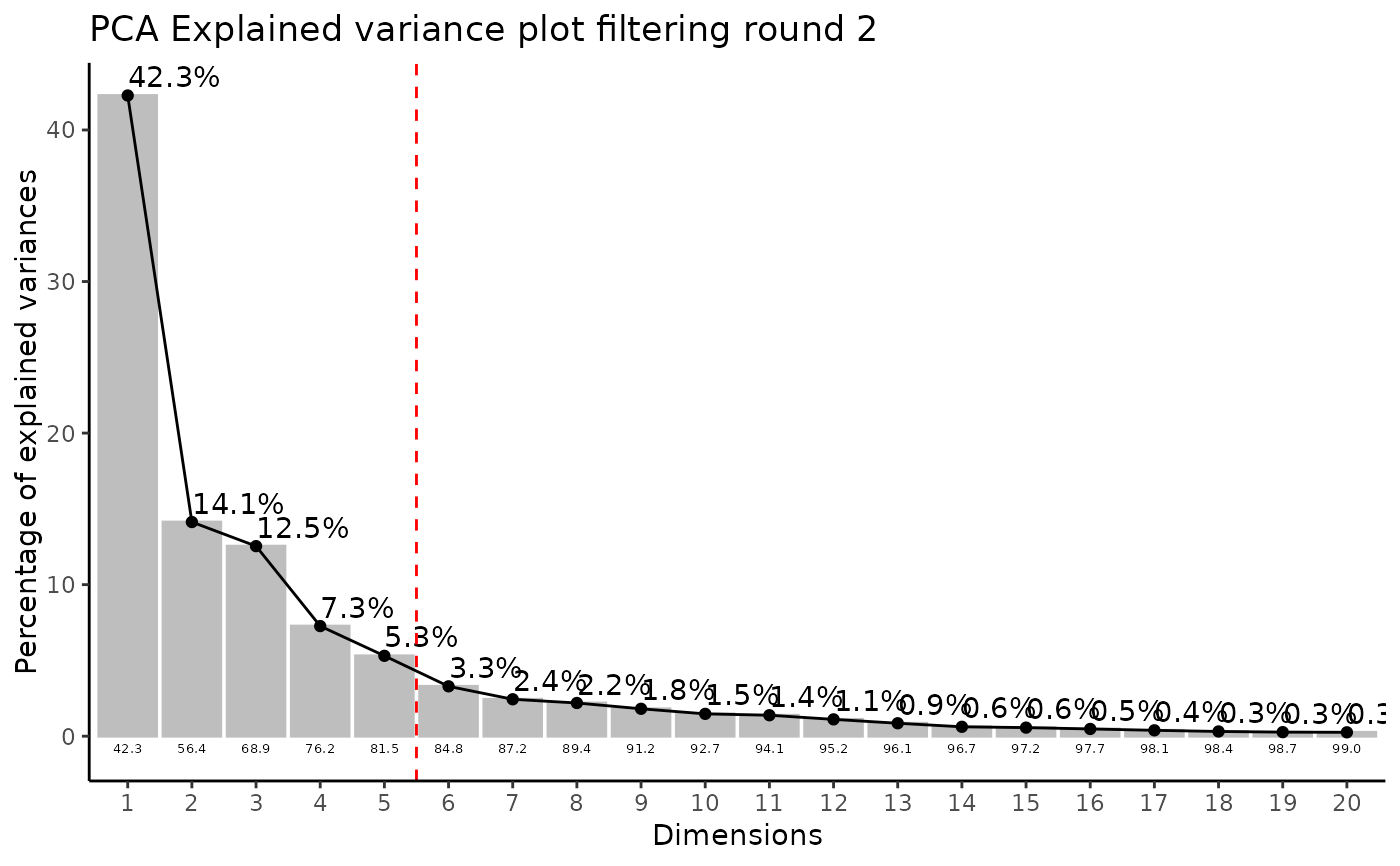
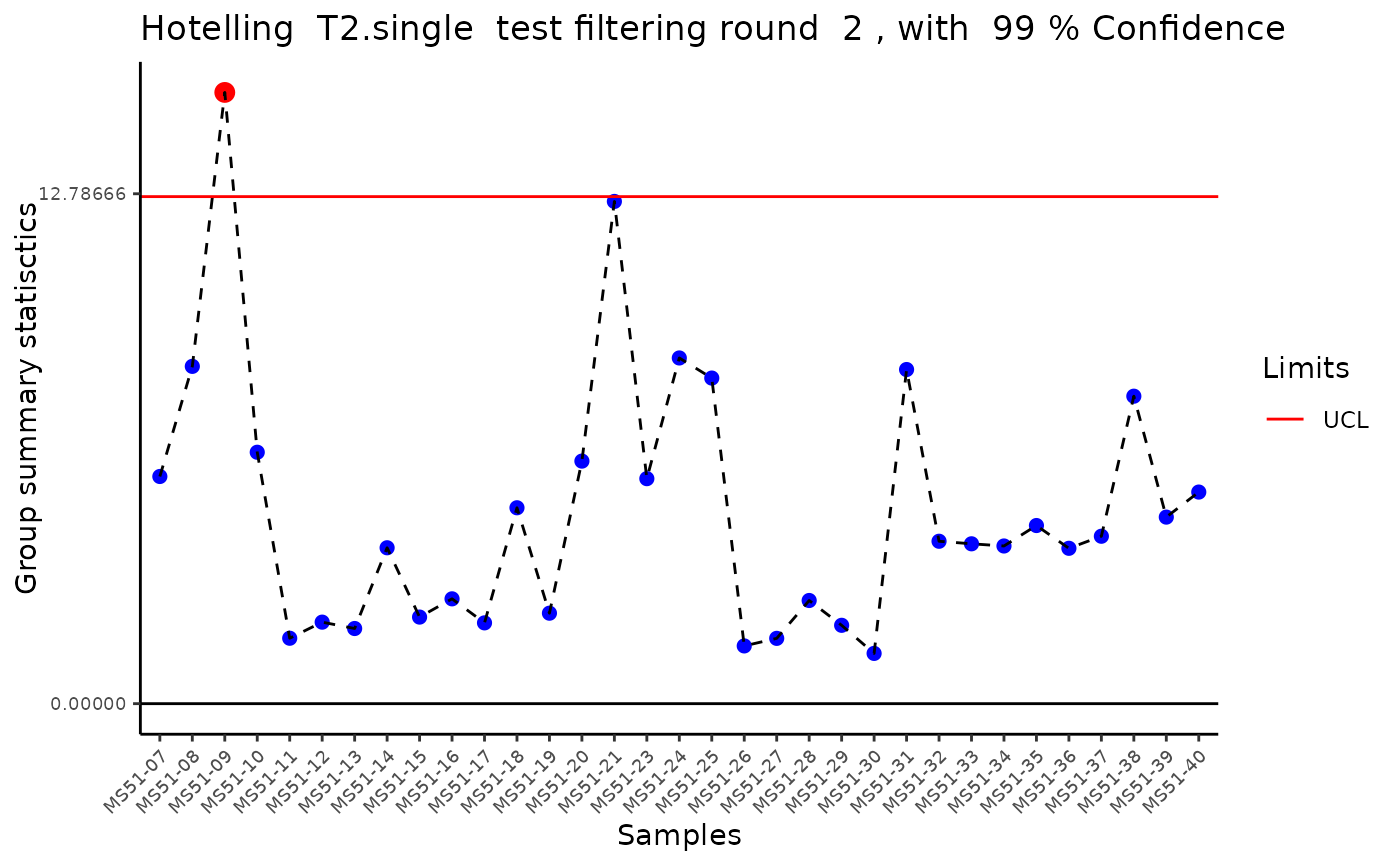
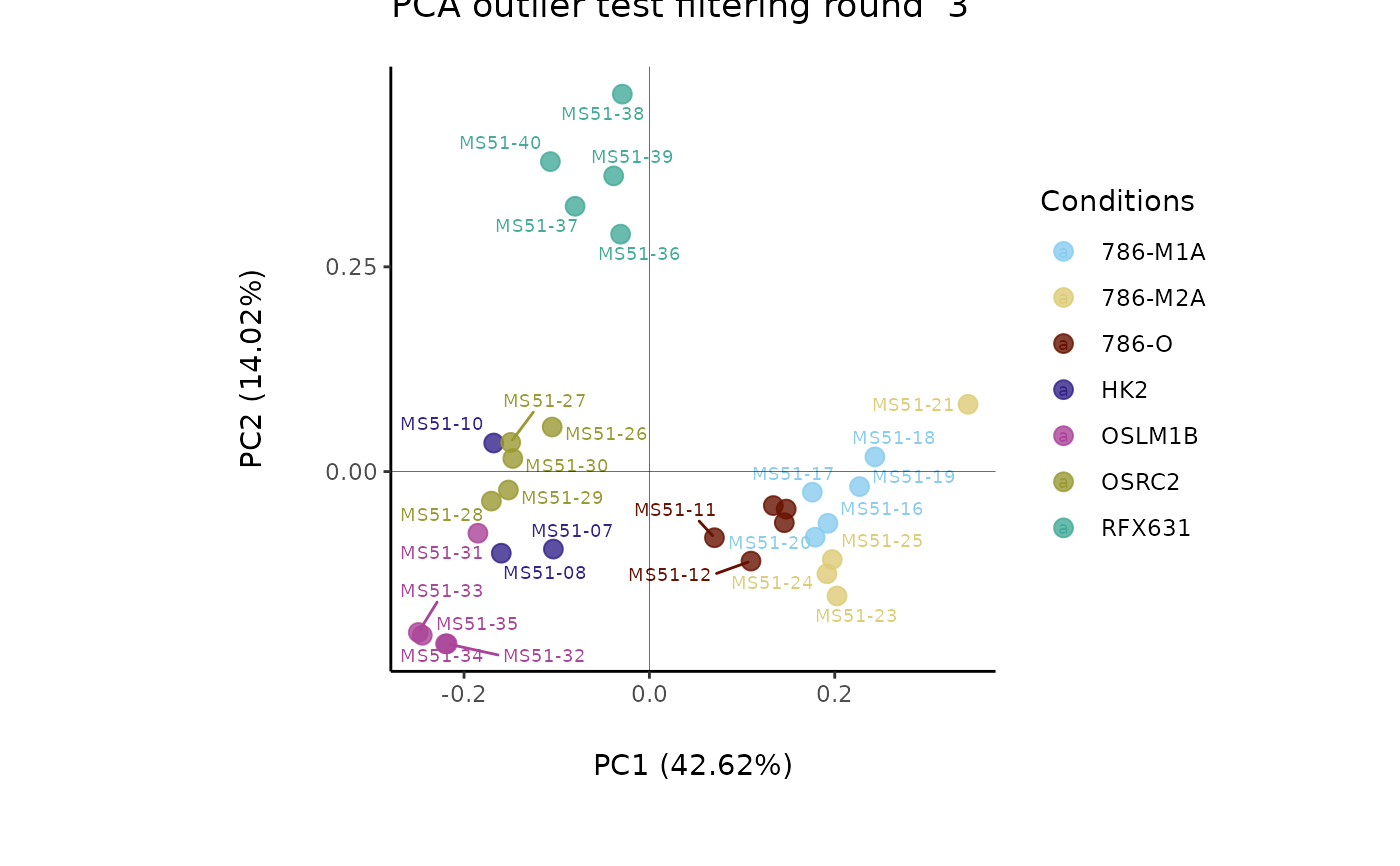
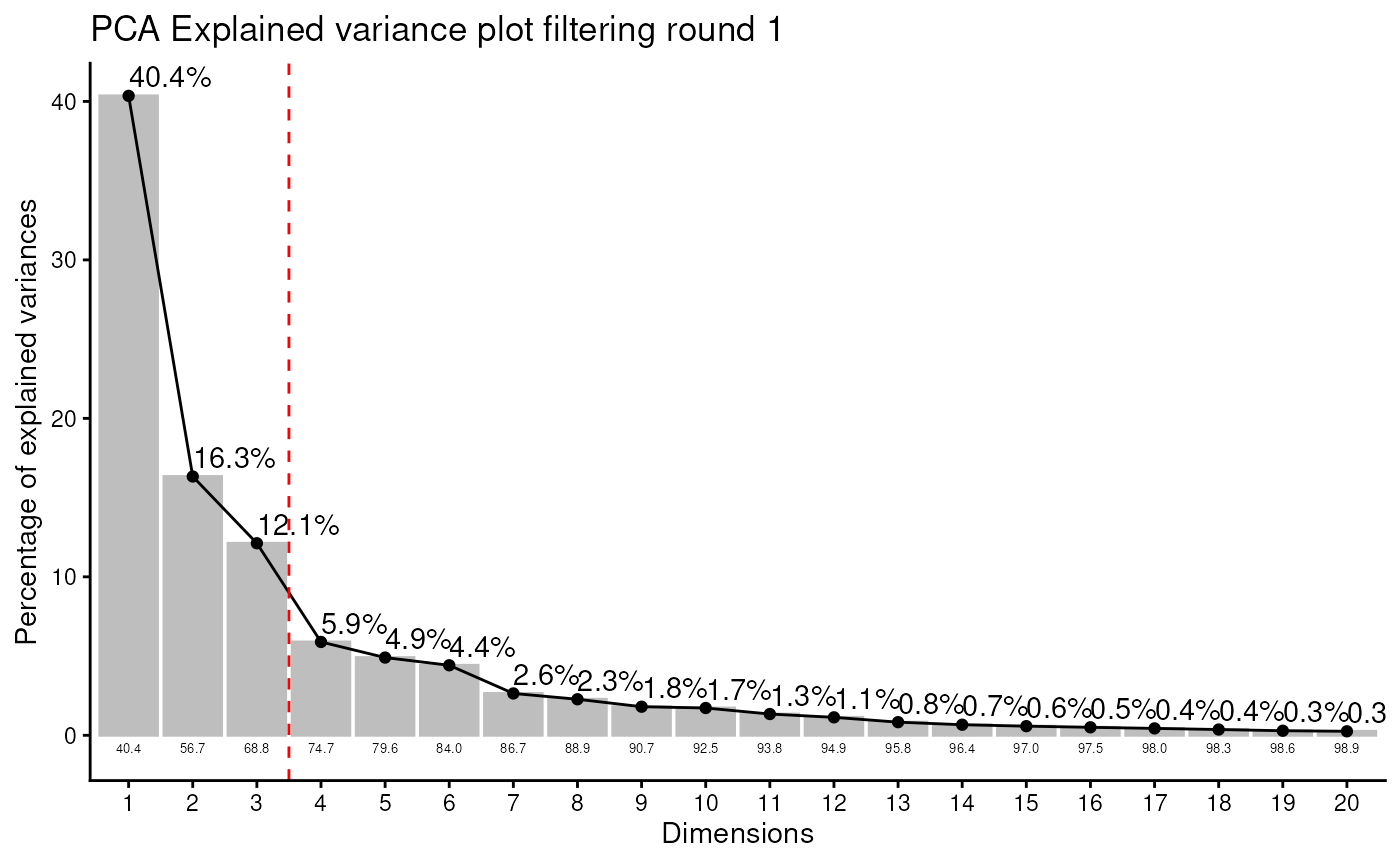
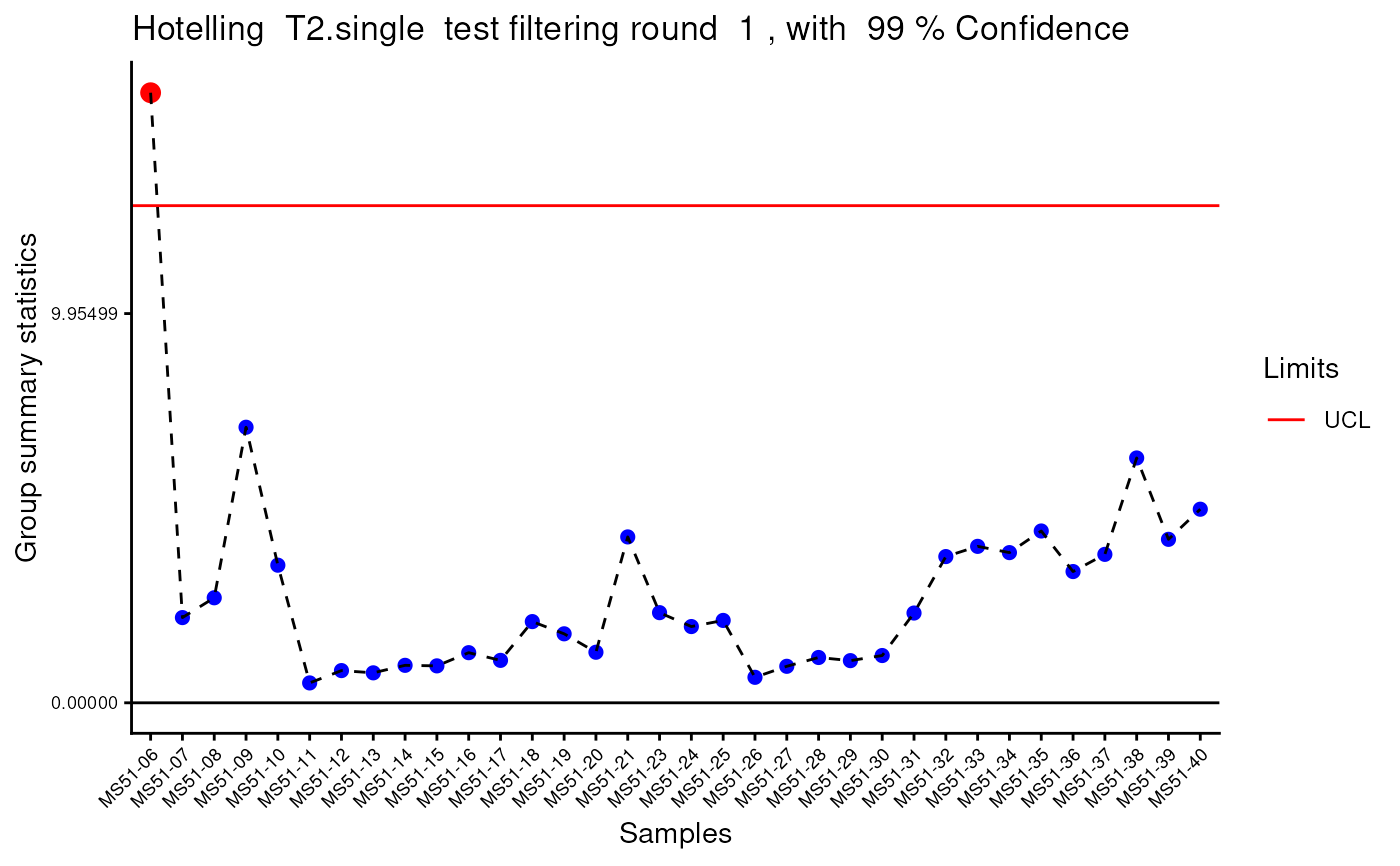
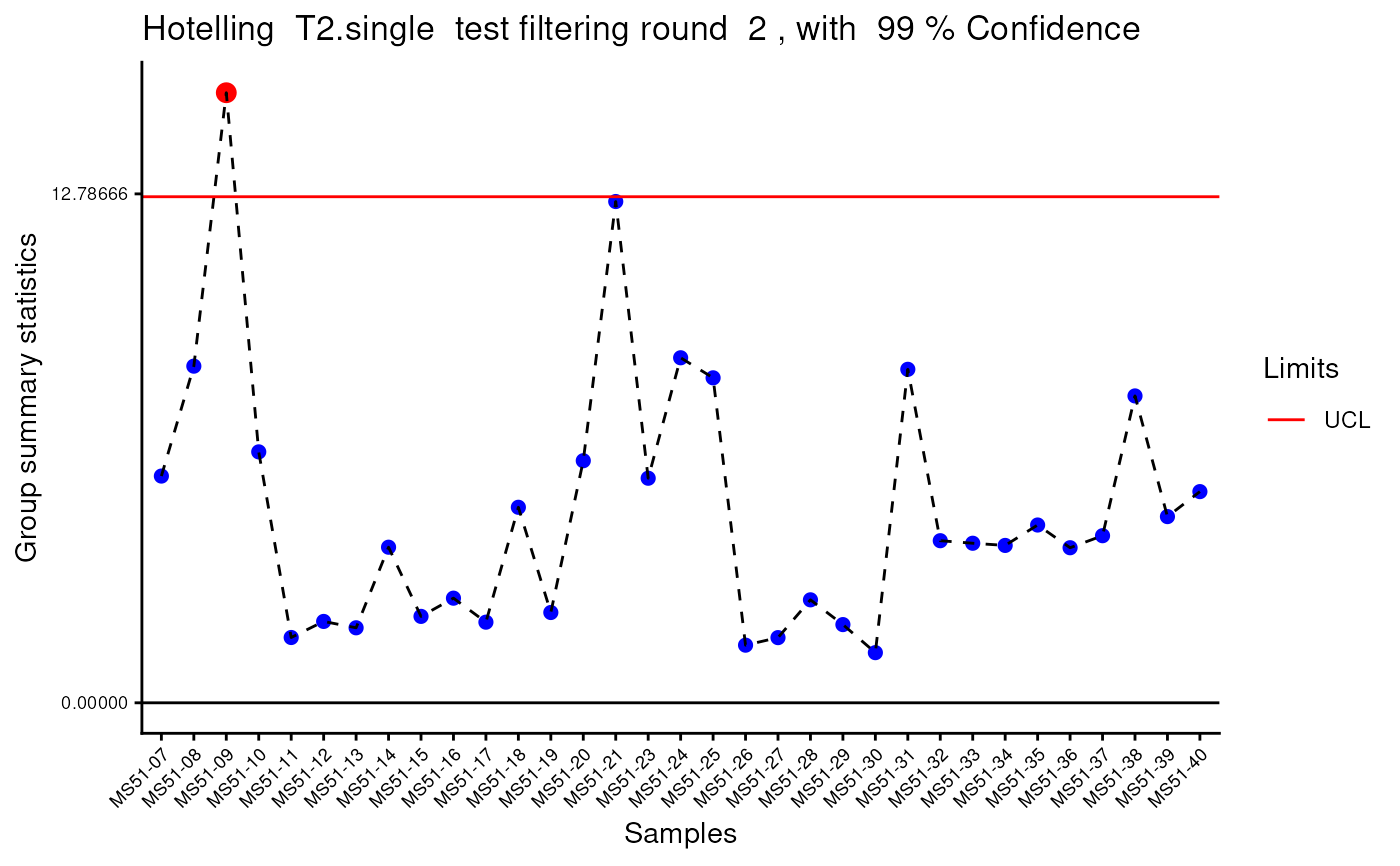
#> Outlier detection: Identification of outlier samples is performed using Hotellin's T2 test to define sample outliers in a mathematical way (Confidence = 0.99 ~ p.val < 0.01) (REF: Hotelling, H. (1931), Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 2 (3), 360-378, doi:https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177732979). hotellins_confidence value selected: 0.99
#> There are possible outlier samples in the data
#> Filtering round 1 Outlier Samples: MS51-06
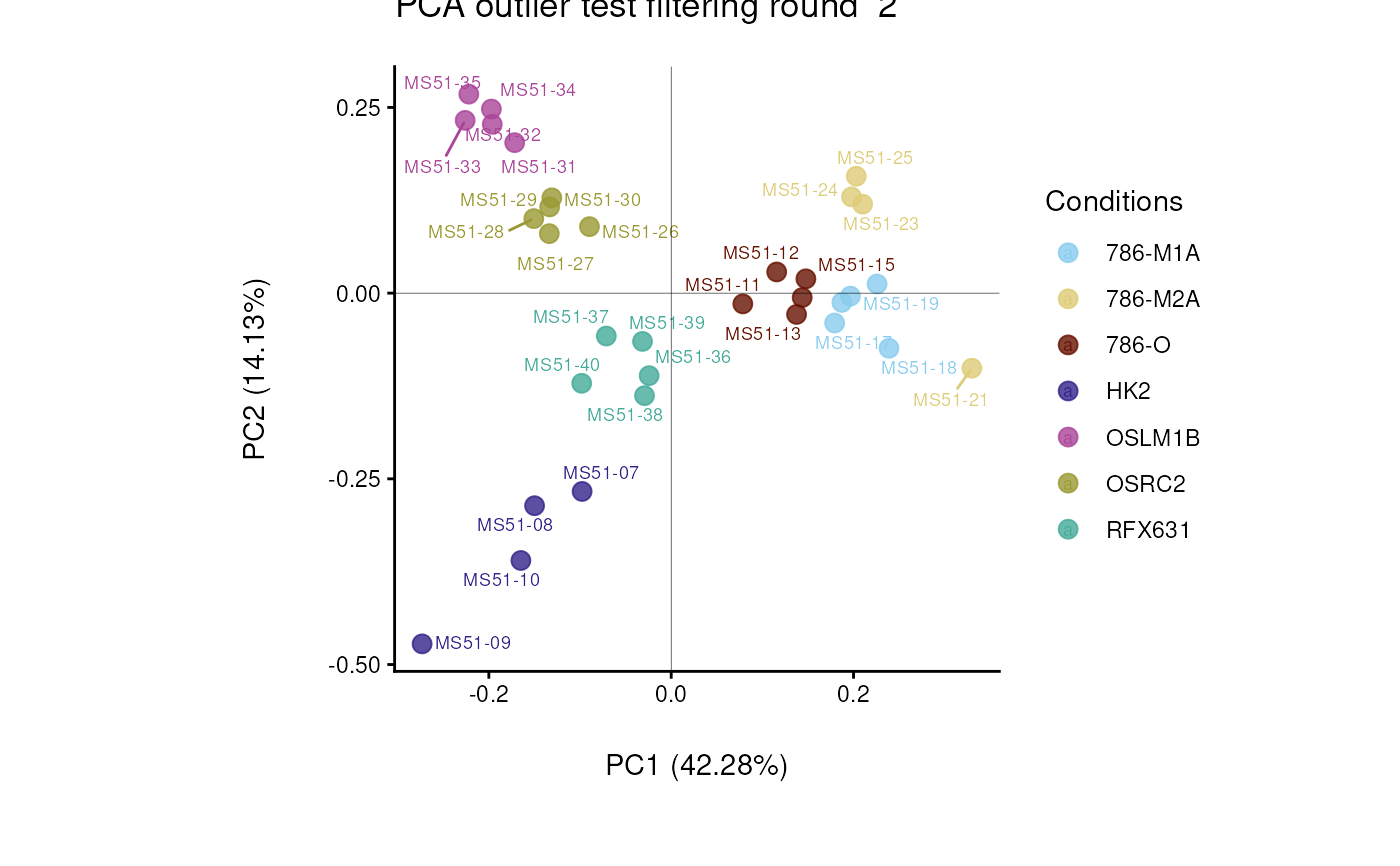
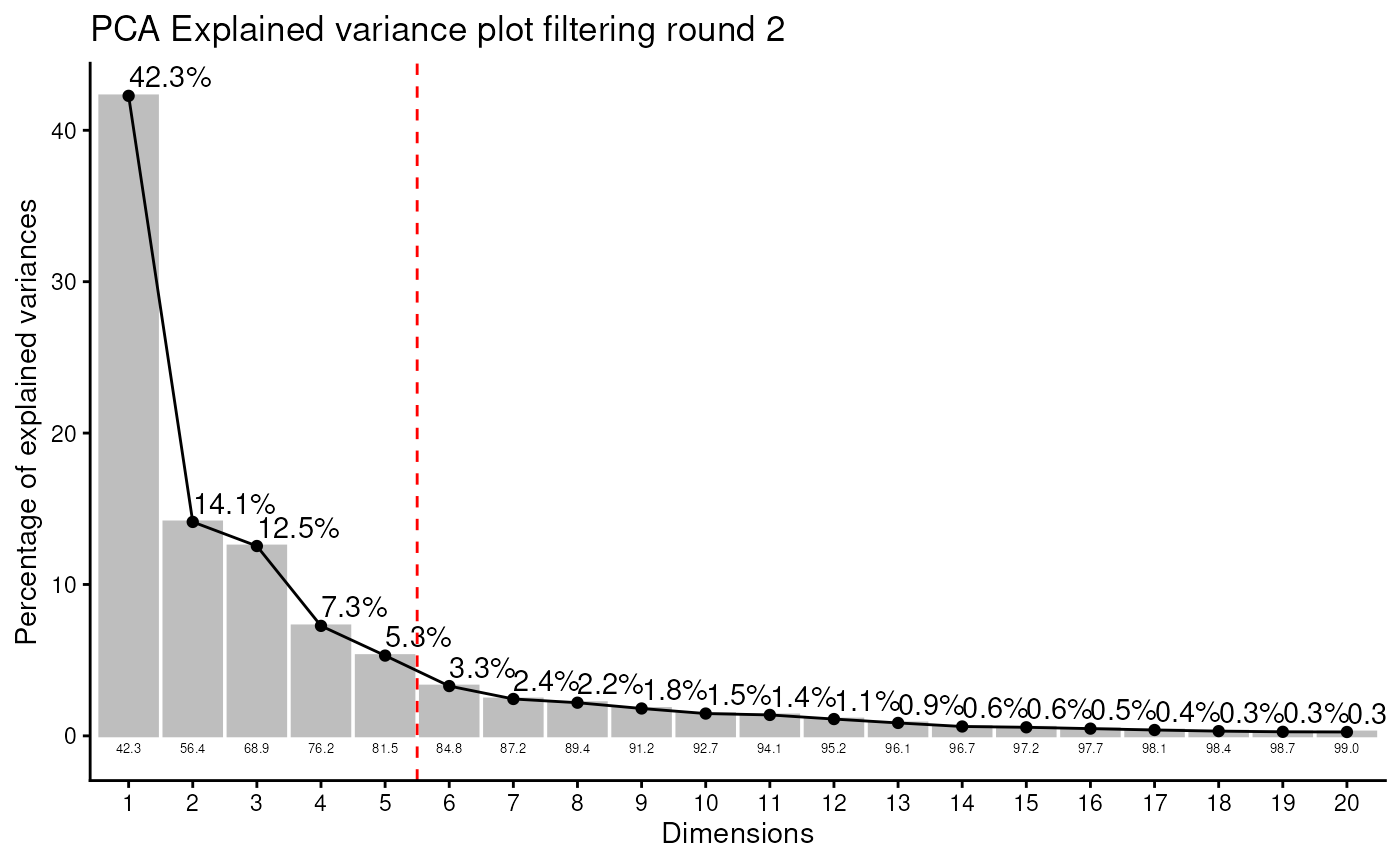
#> Filtering round 2 Outlier Samples: MS51-09
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
data(medium_raw)
Media <- medium_raw %>% tibble::column_to_rownames("Code")
ResM <- processing(
data = Media[-c(40:45), -c(1:3)],
metadata_sample = Media[-c(40:45), c(1:3)],
metadata_info = c(
Conditions = "Conditions",
Biological_Replicates = "Biological_Replicates",
core_norm_factor = "GrowthFactor",
core_media = "blank"
),
core = TRUE
)
#> For Consumption Release experiment we are using the method from Jain M. REF: Jain et. al, (2012), Science 336(6084):1040-4, doi: 10.1126/science.1218595.
#> feature_filtering: Here we apply the modified 80%-filtering rule that takes the class information (Column `Conditions`) into account, which additionally reduces the effect of missing values (REF: Yang et. al., (2015), doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2015.00004). Filtering value selected: 0.8
#> 3 metabolites where removed: N-acetylaspartylglutamate, hypotaurine, S-(2-succinyl)cysteine
#> Missing Value Imputation: Missing value imputation is performed, as a complementary approach to address the missing value problem, where the missing values are imputing using the `half minimum value`. REF: Wei et. al., (2018), Reports, 8, 663, doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-19120-0
#> NA values were found in Control_media samples for metabolites. For metabolites including NAs mvi is performed unless all samples of a metabolite are NA.
#> Metabolites with high NA load (>20%) in Control_media samples are: dihydroorotate.
#> Metabolites with only NAs (= 100%) in Control_media samples are: hydroxyphenylpyruvate. Those NAs are set zero as we consider them true zeros
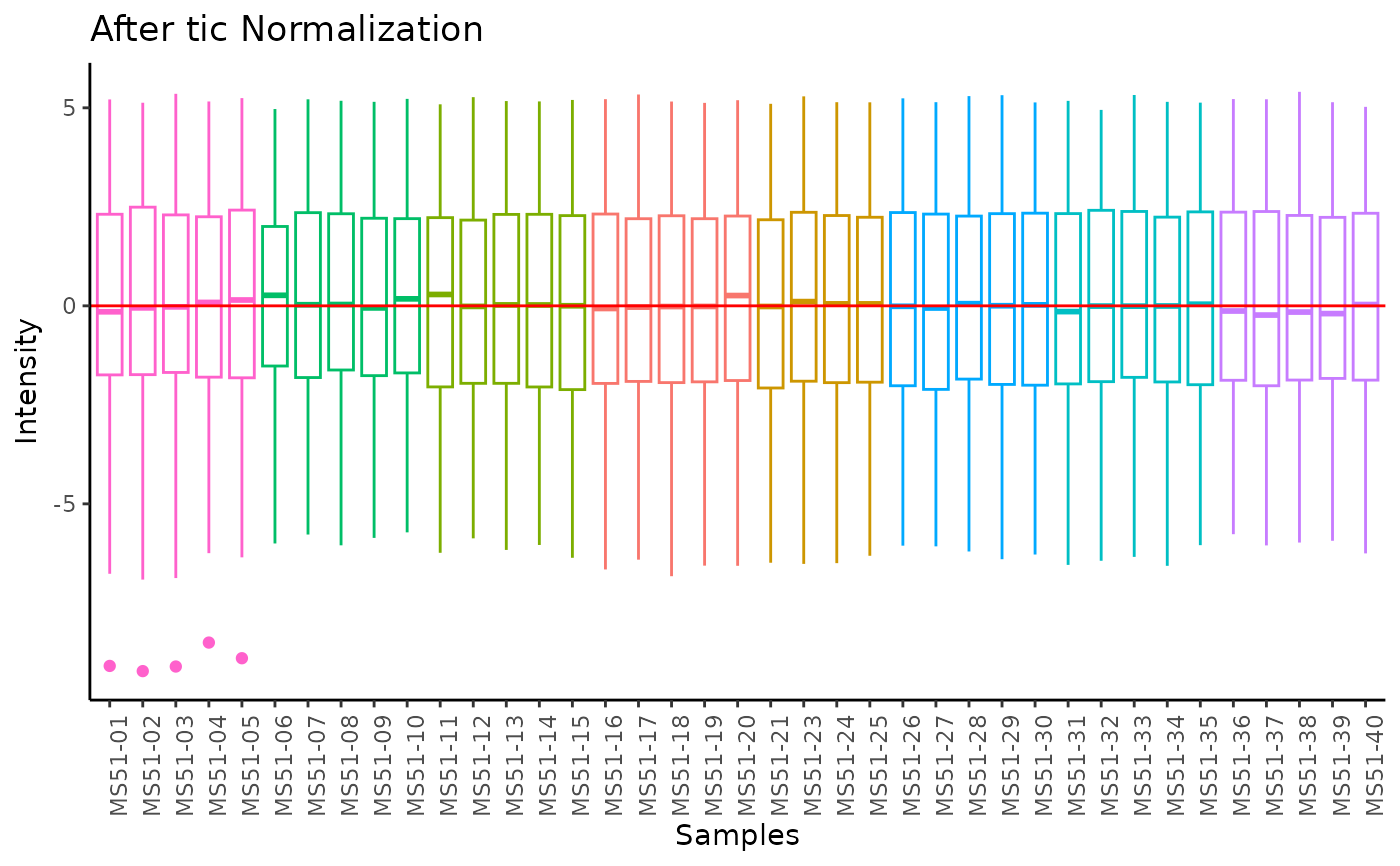
#> total Ion Count (tic) normalization: total Ion Count (tic) normalization is used to reduce the variation from non-biological sources, while maintaining the biological variation. REF: Wulff et. al., (2018), Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 9, 339-351, doi:https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2018.98022
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> 8 of variables have high variability (CV > 30) in the core_media control samples. Consider checking the pooled samples to decide whether to remove these metabolites or not.
#> `stat_bin()` using `bins = 30`. Pick better value `binwidth`.
#> Warning: The following aesthetics were dropped during statistical transformation: label.
#> ℹ This can happen when ggplot fails to infer the correct grouping structure in
#> the data.
#> ℹ Did you forget to specify a `group` aesthetic or to convert a numerical
#> variable into a factor?
#> Bin width defaults to 1/30 of the range of the data. Pick better value with
#> `binwidth`.
#> Warning: The following aesthetics were dropped during statistical transformation: label.
#> ℹ This can happen when ggplot fails to infer the correct grouping structure in
#> the data.
#> ℹ Did you forget to specify a `group` aesthetic or to convert a numerical
#> variable into a factor?
#> Warning: The core_media samples MS51-06 were found to be different from the rest. They will not be included in the sum of the core_media samples.
#> core data are normalised by substracting mean (blank) from each sample and multiplying with the core_norm_factor
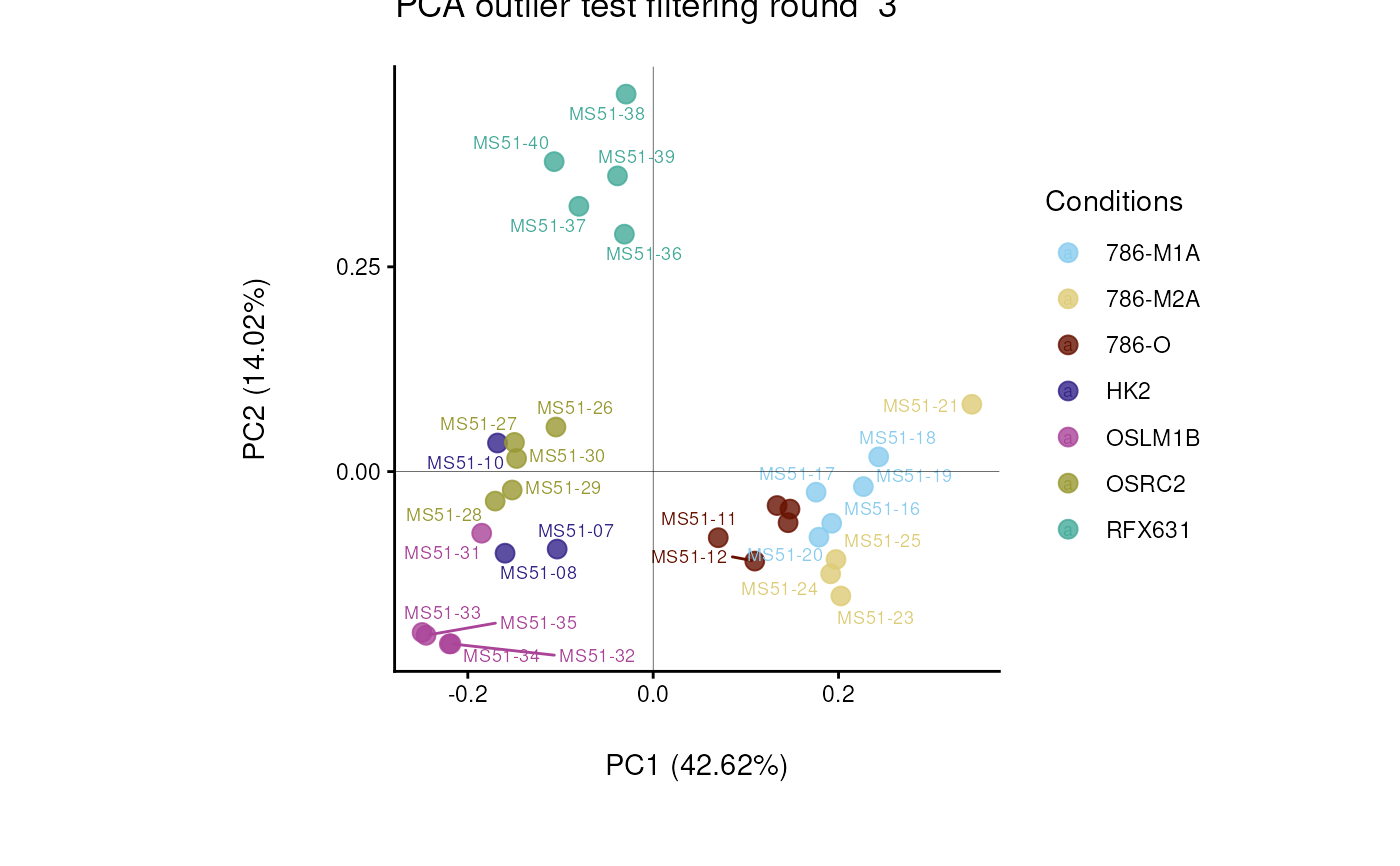
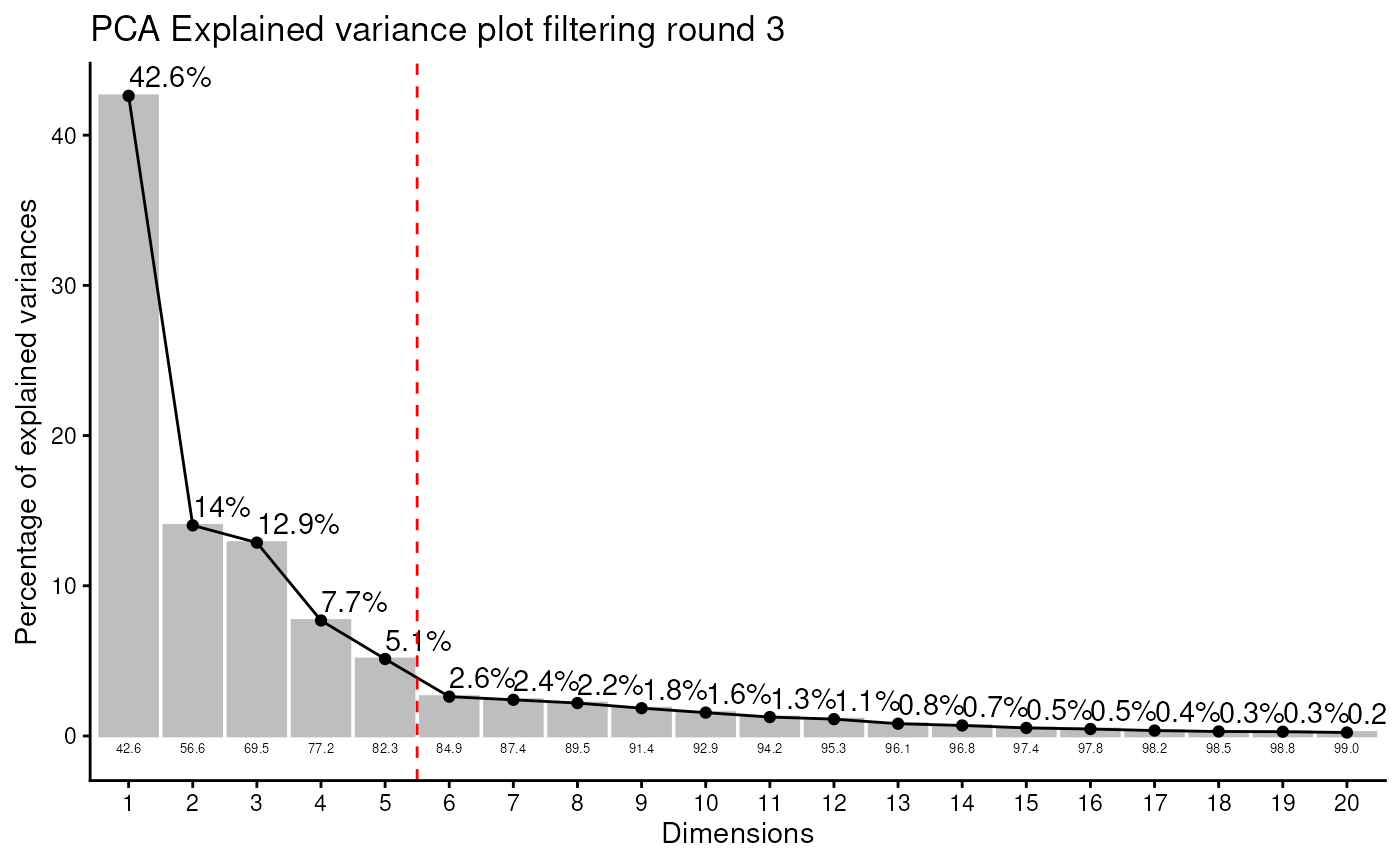
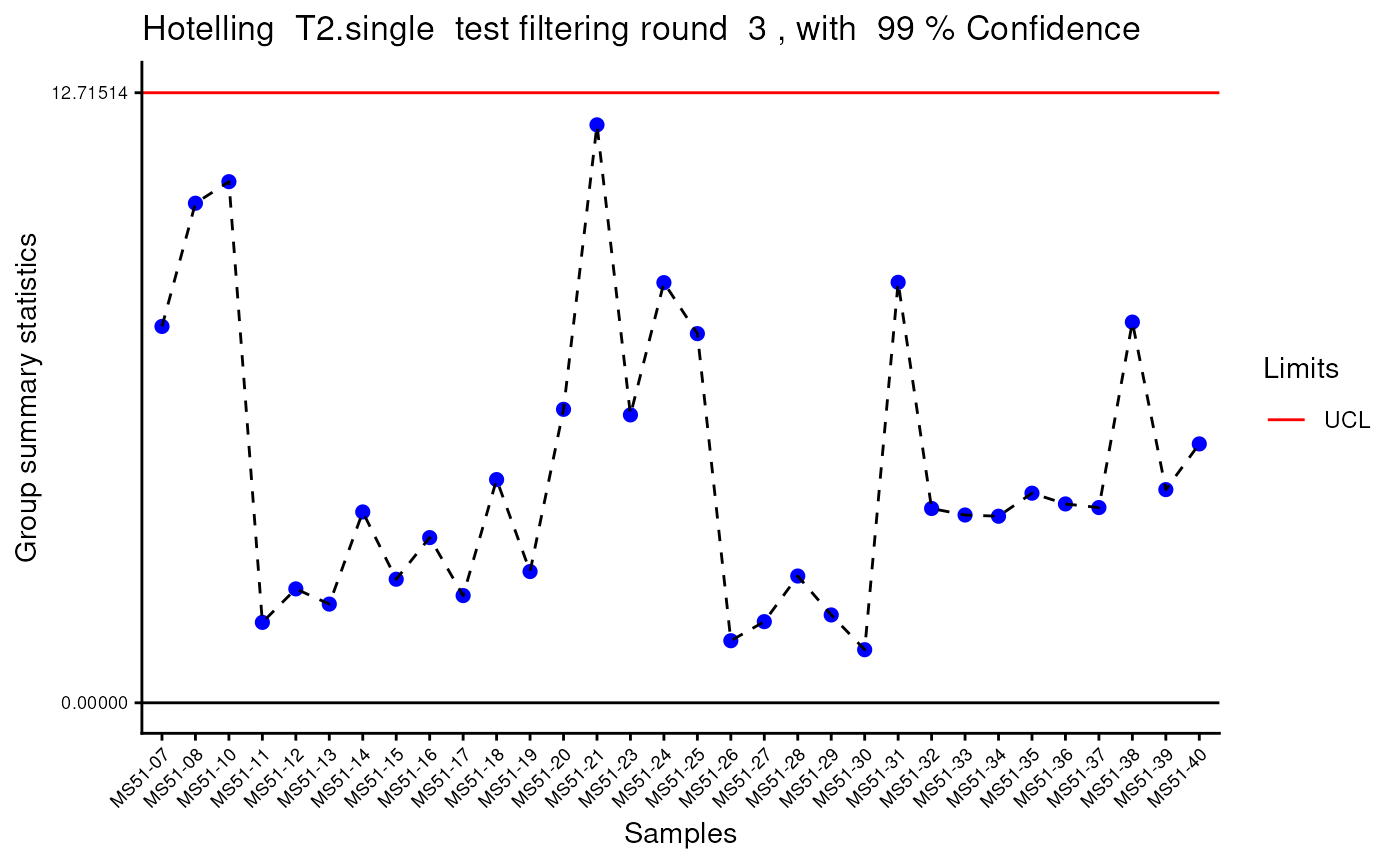
#> Outlier detection: Identification of outlier samples is performed using Hotellin's T2 test to define sample outliers in a mathematical way (Confidence = 0.99 ~ p.val < 0.01) (REF: Hotelling, H. (1931), Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 2 (3), 360-378, doi:https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177732979). hotellins_confidence value selected: 0.99
#> There are possible outlier samples in the data
#> Filtering round 1 Outlier Samples: MS51-06
#> Filtering round 2 Outlier Samples: MS51-09
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
 #> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
 #> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> Warning: ggrepel: 9 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Removed 5 rows containing non-finite outside the scale range
#> (`stat_boxplot()`).
#> Warning: ggrepel: 9 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 9 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 9 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 3 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 3 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 4 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 4 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 3 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 3 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 3 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: ggrepel: 3 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
#> Warning: Ignoring empty aesthetic: `width`.
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 8 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 8 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 10 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 8 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 10 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 8 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
 #> Warning: ggrepel: 10 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps
#> Warning: ggrepel: 10 unlabeled data points (too many overlaps). Consider increasing max.overlaps